Yo, so you’re wondering “Was kostet 1 MWh Strom?” – basically, how much does 1 megawatt-hour of electricity cost? That’s a pretty valid question, man, especially with how much our energy bills are skyrocketing these days. It’s like, “Hey, how much am I actually paying for this juice I’m using?” But it’s not just about the price tag, you know?
It’s about understanding what factors are influencing those costs, like the type of energy sources used, government policies, and even how much demand there is for electricity.
Think of it like this: Electricity prices are like a puzzle, with different pieces coming together to form the final picture. We’ve got different pricing models, energy sources, government regulations, and market forces all playing their part. So, let’s break down this puzzle and see what makes electricity prices tick.
Understanding the Question: Was Kostet 1 Mwh Strom

The question “Was kostet 1 MWh Strom?” translates to “How much does 1 MWh of electricity cost?” in English. This question is fundamental to understanding the cost of energy, particularly for businesses and individuals who consume significant amounts of electricity.
The Meaning of 1 MWh Strom
MWh (megawatt-hour) represents the amount of energy consumed by a device with a power rating of 1 megawatt operating for one hour. To put this into perspective, a typical household might use around 10 kWh (kilowatt-hours) per day, meaning that 1 MWh is equivalent to the energy consumption of 100 households for one day.
Factors Influencing the Price of 1 MWh of Electricity
The price of 1 MWh of electricity is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. These include:
- Energy Source: The cost of generating electricity varies significantly depending on the source. For example, electricity generated from renewable sources like solar and wind is typically cheaper than electricity generated from fossil fuels like coal and natural gas.
- Transmission and Distribution Costs: The cost of transporting electricity from power plants to consumers can add a substantial amount to the final price. Factors like distance, infrastructure, and maintenance contribute to these costs.
- Market Dynamics: The price of electricity is influenced by supply and demand. In times of high demand, the price can rise, while in times of low demand, the price may fall.
- Government Regulations and Taxes: Governments can impose taxes and regulations on the electricity industry, which can impact the final price paid by consumers.
- Fuel Costs: For power plants that rely on fossil fuels, the price of fuel is a major determinant of the cost of electricity. Fluctuations in oil and gas prices can significantly affect the price of electricity.
Electricity Pricing Structures
In Germany, electricity pricing structures are diverse, reflecting the country’s commitment to renewable energy and market liberalization. Understanding these structures is crucial for consumers and businesses alike, as it impacts their electricity costs and choices.
Different Pricing Models
The German electricity market offers various pricing models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Fixed Price Tariffs: These tariffs offer a fixed price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for a specific period, usually a year or longer. This provides price stability and predictability for consumers, making budgeting easier. However, fixed tariffs can be less advantageous if electricity prices decrease significantly during the contract period.
- Variable Price Tariffs: These tariffs fluctuate with wholesale electricity prices, meaning consumers pay a price that reflects the current market conditions. Variable tariffs can be beneficial if wholesale prices fall, but they expose consumers to price volatility and potential increases.
- Dynamic Tariffs: These tariffs adjust based on real-time electricity prices, often influenced by factors like time of day, day of week, and weather conditions. Dynamic tariffs can be more complex but offer the potential for significant savings by consuming electricity during off-peak hours when prices are lower.
- Combined Tariffs: These tariffs combine elements of fixed and variable pricing models, offering a degree of price stability while allowing for some price adjustments based on market conditions.
Comparison of Pricing Models, Was kostet 1 mwh strom
| Pricing Model | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Price Tariffs | Price stability, predictability, easier budgeting | Less advantageous if electricity prices decrease |
| Variable Price Tariffs | Potential for lower prices if wholesale prices fall | Price volatility, potential for higher prices |
| Dynamic Tariffs | Potential for significant savings by consuming during off-peak hours | Complexity, requires monitoring and adjusting consumption patterns |
| Combined Tariffs | Combines elements of fixed and variable pricing, offering some price stability and flexibility | Can be more complex to understand and manage |
Examples of Electricity Tariffs in Germany
- Basic Tariffs: These tariffs are typically offered by traditional energy providers and include a fixed price per kWh, a basic charge, and potentially a surcharge for renewable energy.
- Ökostrom Tariffs: These tariffs specifically focus on electricity generated from renewable sources, often at a slightly higher price than basic tariffs.
- Discount Tariffs: These tariffs offer lower prices for consumers who commit to a longer contract duration or meet certain criteria, such as being a member of a specific organization.
- Time-of-Use Tariffs: These tariffs offer different prices depending on the time of day, with lower prices during off-peak hours and higher prices during peak hours.
Factors Influencing Electricity Prices

Electricity prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including the cost of generating electricity, government policies, and market forces. Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the fluctuations in electricity prices and the challenges faced by consumers and businesses alike.
Energy Sources
The cost of generating electricity is a primary driver of electricity prices. Different energy sources have varying costs, which directly impact the final price consumers pay.
- Fossil Fuels: Coal and natural gas are traditional energy sources that have been widely used for electricity generation. Their prices are influenced by global commodity markets, supply and demand dynamics, and geopolitical factors. For example, fluctuations in oil prices can indirectly impact natural gas prices, affecting electricity generation costs.
- Renewable Energy: Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power have become increasingly competitive. Their costs have been declining steadily due to technological advancements and economies of scale. While renewable energy sources often have lower operating costs, the initial investment in infrastructure can be significant.
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear power plants have high upfront capital costs but relatively low operating costs. However, the safety and waste management concerns associated with nuclear power can influence its cost and regulatory environment.
Current Electricity Prices in Germany
Germany’s electricity market is characterized by a complex interplay of factors, including energy sources, regulatory frameworks, and global market trends. This complexity is reflected in the diverse range of electricity prices across different regions and providers.
Regional Variations in Electricity Prices
Electricity prices in Germany vary significantly across different regions. This variation is influenced by factors such as the availability of local generation sources, transmission infrastructure, and local demand.
- Northern Germany: Typically enjoys lower electricity prices due to its strong reliance on wind energy and access to North Sea offshore wind farms.
- Southern Germany: Often faces higher electricity prices due to a greater reliance on conventional power plants and a higher demand for electricity.
- Eastern Germany: May experience fluctuating prices due to its reliance on lignite-fired power plants and ongoing energy transition efforts.
Comparison of Electricity Prices from Different Providers
The electricity market in Germany is highly competitive, with a multitude of providers offering various tariffs and pricing structures. Comparing electricity prices from different providers can be a complex process, as tariffs often vary based on consumption levels, contract durations, and additional services.
- Large energy companies: Typically offer a range of standard tariffs, often with higher base prices but lower per-kilowatt-hour rates.
- Regional energy suppliers: May focus on renewable energy sources and offer competitive rates for green electricity.
- Online energy comparison platforms: Provide a convenient way to compare prices from multiple providers and identify the best deals.
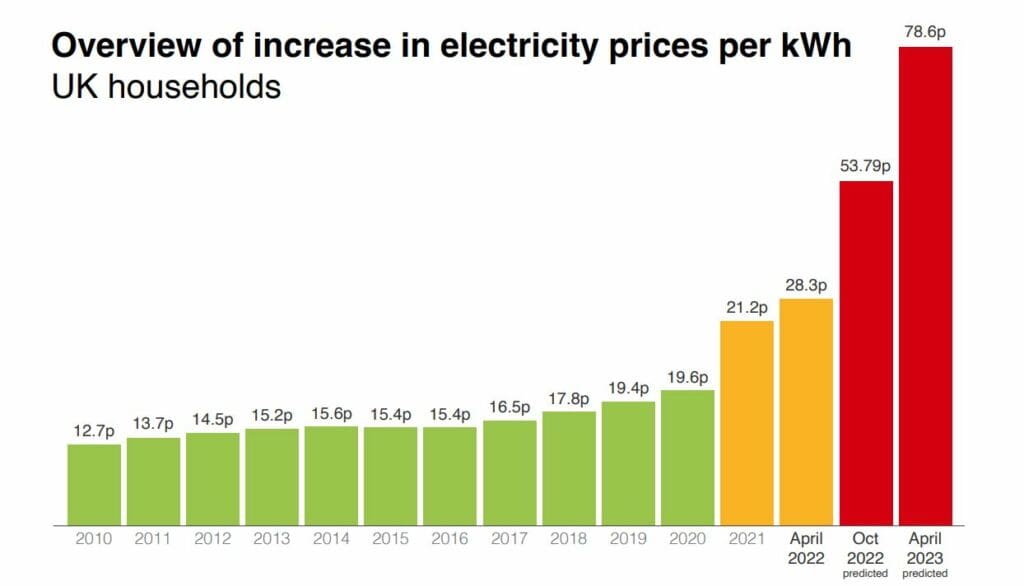
Trends in Electricity Prices over the Past Few Years
Electricity prices in Germany have been subject to significant fluctuations over the past few years. This volatility is driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Increased reliance on renewable energy sources: While contributing to a cleaner energy mix, the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources can lead to price fluctuations.
- Geopolitical events: The ongoing energy crisis, triggered by the conflict in Ukraine, has significantly impacted energy markets, resulting in higher gas prices and, consequently, higher electricity prices.
- Carbon pricing: The introduction of carbon pricing mechanisms has led to higher costs for fossil fuel-based power plants, contributing to higher electricity prices.
Tips for Saving Money on Electricity
Reducing your electricity consumption can significantly lower your energy bills and contribute to a more sustainable future. By implementing practical strategies and embracing energy-efficient technologies, you can achieve substantial savings without compromising comfort.
Energy-Efficient Appliances and Technologies
Investing in energy-efficient appliances and technologies is a smart way to reduce your electricity consumption and save money in the long run. These appliances are designed to use less energy while maintaining or even improving performance.
- LED Lighting: LED lights consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, offering substantial savings on your electricity bill. They also last much longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Energy-Efficient Refrigerators: Modern refrigerators with energy-efficient ratings use less energy to keep your food cold. Look for models with features like automatic defrosting and insulation that minimizes heat loss.
- Smart Thermostats: Smart thermostats can learn your heating and cooling preferences and adjust the temperature accordingly, optimizing energy usage and reducing your energy bills.
- Energy-Efficient Washing Machines and Dryers: High-efficiency washing machines use less water and energy to clean your clothes, while energy-efficient dryers utilize heat pumps or other technologies to minimize energy consumption.
So, there you have it, man. Electricity prices are a complex thing, but by understanding the factors that influence them, we can make smarter choices about our energy consumption. Whether it’s about choosing energy-efficient appliances, switching to renewable energy, or simply being more mindful of our energy usage, there are things we can do to keep those electricity bills in check.
It’s all about being informed, making conscious choices, and maybe even saving a few bucks in the process. Peace out!
Quick FAQs
How often do electricity prices change in Germany?
Electricity prices in Germany can change quite frequently, sometimes even monthly, depending on the provider and tariff you choose. It’s a good idea to check your tariff regularly to see if there are any changes.
Are there any government subsidies for renewable energy in Germany?
Yes, there are various government subsidies and incentives available for renewable energy in Germany, like the “EEG” (Renewable Energy Sources Act). These programs can help offset the cost of installing solar panels or wind turbines.





