Was kostet Strom tanken? This question, translated as “How much does it cost to charge an electric vehicle?”, is at the forefront of many minds as the world embraces sustainable transportation. Understanding the cost of charging an electric vehicle is crucial for making informed decisions about switching to this eco-friendly option. The cost of charging depends on a variety of factors, including the electricity tariffs in your region, the type of charging station used, the time spent charging, and the battery capacity of your vehicle.
This guide will delve into the intricacies of electric vehicle charging costs, providing insights into the factors that influence them, methods for calculating them, and a comparison with traditional fuel vehicles. We will also explore the impact of government incentives and future trends in the evolving landscape of electric vehicle charging.
Understanding “Was kostet Strom tanken?”

“Was kostet Strom tanken?” translates to “How much does it cost to charge an electric car?” in English. This is a question many people ask when considering switching to an electric vehicle. The cost of charging an electric car is influenced by various factors, and it’s essential to understand these factors to make informed decisions.
Factors influencing charging costs
The cost of charging an electric vehicle depends on several factors, including:
- Electricity tariff: Your electricity provider’s tariff determines the price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) you pay. Some tariffs offer cheaper rates during off-peak hours, which can significantly reduce charging costs.
- Charging location: Public charging stations often charge higher rates than home charging. Some public charging stations offer different pricing tiers based on charging speed.
- Vehicle efficiency: Different electric vehicles have varying energy consumption rates. Vehicles with higher efficiency use less electricity to travel the same distance, leading to lower charging costs.
- Battery capacity: The size of your electric vehicle’s battery determines how much energy it can store. Larger batteries require more electricity to fully charge, resulting in higher costs.
- Charging method: The method you use to charge your electric car also affects the cost. Level 1 charging, using a standard household outlet, is the slowest but typically the cheapest. Level 2 charging, using a dedicated charging station, is faster and generally more expensive. DC fast charging, the fastest option, is the most expensive but can fully charge your battery in minutes.
Charging method cost comparison
Here’s a comparison of different charging methods and their associated costs:
| Charging Method | Charging Speed | Typical Cost per kWh | Typical Charging Time (for a 60 kWh battery) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 Charging | Slowest | $0.10 – $0.20 | 12-24 hours |
| Level 2 Charging | Faster | $0.15 – $0.30 | 4-8 hours |
| DC Fast Charging | Fastest | $0.40 – $1.00 | 20-40 minutes |
Factors Affecting Charging Costs
Charging an electric vehicle is a cost-effective way to fuel your car, but the price can vary depending on several factors. Let’s dive into the key elements that influence how much you’ll spend on charging your EV.
Electricity Tariffs
Electricity tariffs play a significant role in determining charging costs. They’re the price you pay per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity consumed. Different electricity providers offer various tariffs, each with its own pricing structure.
- Time-of-Use Tariffs: These tariffs offer lower rates during off-peak hours (typically overnight) and higher rates during peak hours (usually during the day). This can be a cost-effective option if you can charge your EV overnight, taking advantage of cheaper electricity prices.
- Flat-Rate Tariffs: These tariffs charge a consistent price per kWh, regardless of the time of day. They offer simplicity but may not be as cost-effective as time-of-use tariffs if you can take advantage of off-peak pricing.
Home vs. Public Charging
The location where you charge your EV can also affect the cost.
- Home Charging: Charging at home is generally the most affordable option. You’re likely to have a lower electricity tariff than public charging stations. Additionally, you can take advantage of time-of-use tariffs to minimize your charging costs.
- Public Charging Stations: Public charging stations often charge higher rates than home charging. They typically have a higher electricity tariff to cover their operating costs and provide convenience. However, public charging stations can be useful when you’re on the road and need to top up your battery quickly.
Charging Time and Battery Capacity
The time it takes to charge your EV and the capacity of your vehicle’s battery also impact charging costs.
- Charging Time: The longer you charge your EV, the more electricity you’ll consume, leading to higher costs. However, charging overnight on a time-of-use tariff can significantly reduce your overall charging costs.
- Battery Capacity: Vehicles with larger battery capacities require more electricity to charge fully, resulting in higher charging costs. However, larger batteries offer a longer driving range, which can be advantageous for long trips.
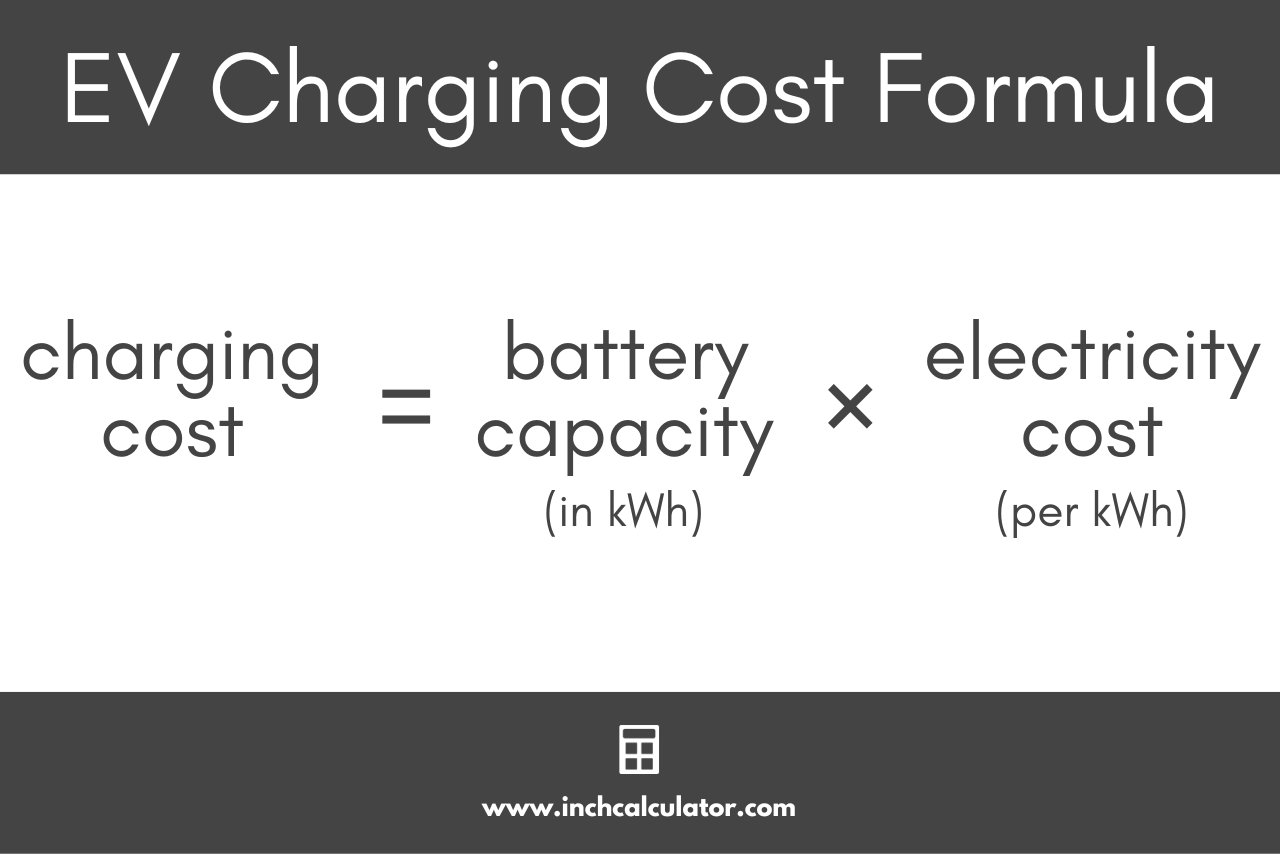
Calculating Charging Costs

Knowing the cost of charging your electric vehicle is crucial for budgeting and planning your trips. This section will guide you through calculating your charging costs, considering electricity tariffs and vehicle battery capacity.
Calculating Charging Costs
To calculate the cost of charging your electric vehicle, you need to know the following:
Electricity tariff
This is the price you pay per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity. Your electricity provider should provide this information on your bill or website.
Vehicle battery capacity
This is the amount of energy your vehicle’s battery can store, measured in kWh. You can find this information in your vehicle’s manual or online.
Charging efficiency
This refers to the percentage of energy that is actually transferred from the charging station to your vehicle’s battery. Most modern EVs have a charging efficiency of around 85-95%.
Charging Cost = (Battery Capacity
Electricity Tariff) / Charging Efficiency
For example, let’s say you have a vehicle with a 60 kWh battery, your electricity tariff is $0.15 per kWh, and your charging efficiency is 90%. The cost of charging your vehicle from completely empty to full would be:
(60 kWh – $0.15/kWh) / 0.90 = $10
Charging Costs for Different Vehicle Models and Distances
The following table shows the estimated cost of charging different vehicle models for various distances, assuming an average electricity tariff of $0.15 per kWh and a charging efficiency of 90%:| Vehicle Model | Battery Capacity (kWh) | Distance (miles) | Charging Cost ($) ||—|—|—|—|| Tesla Model 3 | 75 | 250 | $12.50 || Chevrolet Bolt | 60 | 238 | $10.00 || Nissan Leaf | 40 | 150 | $6.67 || Hyundai Kona Electric | 64 | 258 | $10.67 |It’s important to note that these are just estimates and the actual cost may vary depending on your specific electricity tariff, charging efficiency, and driving conditions.
Tips for Estimating Charging Costs
Use online charging cost calculators
Several websites and apps allow you to estimate charging costs based on your vehicle model, electricity tariff, and distance.
Check your electricity bill
Your electricity bill will show your current electricity tariff.
Monitor your charging sessions
Keep track of how much energy you use during each charging session and the cost. This will help you understand your charging habits and budget accordingly.
Consider time-of-use tariffs
Some electricity providers offer time-of-use tariffs that charge lower rates during off-peak hours. This can save you money on charging costs.
Cost Comparison with Fuel Vehicles
So you’re considering switching to an electric vehicle, but you’re wondering if it’s really worth it financially? Well, buckle up, because we’re about to dive into the world of cost comparisons and see if electric vehicles can truly save you some dough.Let’s break down the cost of charging an electric vehicle versus fueling a traditional gasoline or diesel car. We’ll explore the long-term savings associated with electric vehicle ownership and provide some real-world examples to illustrate the cost differences.
Cost Comparison: Charging vs. Fueling
The cost of charging an electric vehicle is significantly lower than the cost of fueling a gasoline or diesel car. This is because electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline or diesel, and electric vehicles are much more energy-efficient.For instance, let’s compare a typical gasoline car with a fuel efficiency of 30 miles per gallon (mpg) to an electric vehicle with a range of 250 miles.
Assuming a gasoline price of $4 per gallon and an electricity cost of $0.12 per kilowatt-hour (kWh), the cost of driving 100 miles would be:* Gasoline car: 100 miles / 30 mpg = 3.33 gallons of gasoline$4/gallon = $13.32
Electric vehicle
Assuming an average energy consumption of 0.3 kWh/mile, 100 miles
- 0.3 kWh/mile = 30 kWh
- $0.12/kWh = $3.60
This example shows that the cost of driving 100 miles in an electric vehicle is significantly lower than the cost of driving the same distance in a gasoline car.
Long-Term Cost Savings, Was kostet strom tanken
The cost savings associated with electric vehicle ownership go beyond just the cost of fueling. Electric vehicles require less maintenance than gasoline cars, as they have fewer moving parts. This translates to lower maintenance costs over the long term.Additionally, electric vehicles are eligible for various government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, which can further reduce the overall cost of ownership.
Real-World Scenarios
Let’s look at some real-world scenarios to illustrate the cost savings of owning an electric vehicle:* Daily Commute: Imagine a daily commute of 50 miles round trip. A gasoline car with 30 mpg would consume 1.67 gallons of gasoline per day, costing approximately $6.68 at $4 per gallon. An electric vehicle with a range of 250 miles and an energy consumption of 0.3 kWh/mile would require 15 kWh of electricity per day, costing around $1.80 at $0.12 per kWh.
This equates to a daily savings of $4.88 for the electric vehicle.* Road Trip: For a 500-mile road trip, a gasoline car with 30 mpg would consume 16.67 gallons of gasoline, costing approximately $66.68 at $4 per gallon. An electric vehicle with a range of 250 miles and an energy consumption of 0.3 kWh/mile would require 150 kWh of electricity, costing around $18 at $0.12 per kWh.
This equates to a savings of $48.68 for the electric vehicle.These real-world scenarios demonstrate the substantial cost savings that electric vehicle ownership can offer.
Impact of Government Incentives
Government incentives play a significant role in making electric vehicle charging more affordable and accessible. These incentives can come in various forms, including subsidies, tax breaks, and rebates, and their impact can be substantial, influencing both the initial purchase cost of an EV and the ongoing charging expenses.
Availability of Incentives in Different Regions
The availability and structure of government incentives for EV charging vary significantly across different regions.
- United States: The U.S. offers federal tax credits for the purchase of new electric vehicles, with varying amounts depending on the vehicle’s battery capacity and manufacturer. Several states also offer additional incentives, including rebates, tax credits, and exemptions from sales tax. For example, California offers a $2,000 rebate for the purchase of a new EV.
- European Union: The EU has implemented a range of policies to promote electric vehicle adoption, including subsidies for charging infrastructure and tax breaks for EV purchases. Individual member states often have their own additional incentives, such as tax breaks and subsidies for home charging installations. For instance, Germany offers a substantial subsidy for home charging installations, significantly reducing the upfront cost for EV owners.
- China: China has emerged as a global leader in electric vehicle adoption, driven by significant government support. The Chinese government provides generous subsidies for EV purchases and charging infrastructure development. Additionally, many cities offer free or discounted parking for EVs and prioritize charging station installation in public areas.
Benefits of Government Incentives
Government incentives for EV charging offer several key benefits:
- Reduced Charging Costs: Incentives can directly reduce the cost of charging, making it more affordable for EV owners. This can be achieved through rebates on home charging installations, subsidies for public charging stations, or tax breaks on electricity used for charging.
- Increased EV Adoption: By making EVs more affordable, government incentives can encourage more people to switch from gasoline-powered vehicles. This can lead to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality.
- Stimulation of the EV Industry: Incentives can help to stimulate the growth of the EV industry by creating demand for EVs and charging infrastructure. This can lead to innovation and the development of new technologies, further driving down the cost of EVs and charging.
Potential for Future Changes in Government Policies
As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow, governments are likely to adjust their incentive programs to reflect changing market conditions and policy priorities.
- Increased Focus on Charging Infrastructure: Governments may prioritize incentives for the development of public charging infrastructure, ensuring that EV owners have access to reliable and convenient charging options.
- Transition to Performance-Based Incentives: Some governments may shift from upfront purchase incentives to performance-based incentives, such as rebates based on the number of miles driven or the amount of emissions reduced. This approach could encourage the adoption of EVs with longer ranges and higher efficiency.
- Integration with Smart Grid Technologies: As smart grid technologies become more prevalent, governments may introduce incentives that encourage the integration of EV charging with renewable energy sources and demand response programs. This could help to optimize grid stability and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Future Trends in Charging Costs: Was Kostet Strom Tanken
The cost of charging an electric vehicle is a significant factor in the decision-making process for many potential buyers. The future of charging costs is influenced by a combination of factors, including the price of electricity, advancements in charging technologies, and government policies.
Electricity Price Fluctuations
The price of electricity is a key determinant of charging costs. While the price of electricity is subject to volatility, several factors can impact its future trajectory.
- Increased renewable energy adoption: The growing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power has the potential to reduce electricity prices in the long term, as these sources become more cost-effective. For example, the cost of solar panels has dropped significantly in recent years, making solar power a more attractive option for both residential and commercial consumers. This could lead to lower electricity prices, ultimately reducing charging costs for electric vehicle owners.
- Demand for electricity: The demand for electricity is expected to increase as the adoption of electric vehicles and other electrified technologies continues to grow. This increased demand could potentially lead to higher electricity prices. However, smart grid technologies and energy storage solutions can help to manage demand and mitigate potential price increases. For instance, electric vehicle charging can be scheduled during off-peak hours, when electricity prices are typically lower, reducing the overall charging costs.
- Government policies and subsidies: Government policies and subsidies can play a significant role in shaping the cost of electricity. For example, tax credits and incentives for renewable energy projects can encourage investment in clean energy, potentially lowering electricity prices. However, government policies can also impact electricity prices through regulations and taxes. For example, carbon taxes or fees on fossil fuels can increase the cost of electricity generation, leading to higher prices for consumers.
Evolution of Charging Technologies
The rapid development of new charging technologies is influencing the landscape of electric vehicle charging costs.
- Faster charging speeds: Charging technologies are continuously evolving to offer faster charging speeds. The development of fast-charging stations with high-power outputs, such as those with direct current (DC) fast charging capabilities, allows for quicker charging times. This can significantly reduce the time spent charging and potentially lower the overall cost of charging. For example, some fast-charging stations can add up to 200 miles of range in just 30 minutes.
However, these fast-charging stations are often more expensive to build and operate, which can result in higher charging costs for users.
- Wireless charging: Wireless charging technology offers a more convenient and potentially less expensive way to charge electric vehicles. Instead of plugging in a cable, vehicles can be charged wirelessly by placing them on a charging pad. This technology is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to become more affordable and widespread in the future.
Wireless charging could potentially eliminate the need for costly charging stations and infrastructure, leading to lower charging costs.
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology: V2G technology enables electric vehicles to act as energy storage devices, selling excess energy back to the grid. This can provide a revenue stream for electric vehicle owners and potentially reduce the cost of charging. For example, electric vehicles can be charged during off-peak hours when electricity prices are low and then discharge energy back to the grid during peak hours, when prices are higher.
This can help to manage grid demand and potentially reduce overall charging costs.
In conclusion, the cost of charging an electric vehicle is a multifaceted topic that requires careful consideration. While initial costs may seem higher compared to traditional fuel vehicles, the long-term savings, government incentives, and the environmental benefits make electric vehicles a compelling choice. As technology advances and charging infrastructure expands, the cost of charging is expected to become even more competitive, further accelerating the transition to sustainable transportation.
Understanding the factors that influence charging costs, utilizing available resources for calculating them, and staying informed about future trends will empower you to make informed decisions about your electric vehicle charging needs.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the average cost of charging an electric vehicle?
The average cost of charging an electric vehicle varies depending on factors such as electricity tariffs, charging station type, and vehicle battery capacity. However, it is generally lower than the cost of fueling a gasoline or diesel vehicle.
How do I find the cheapest charging stations?
Several apps and websites provide information on charging station locations, prices, and availability. You can also check with your local utility company or electric vehicle manufacturer for recommendations.
Are there any government incentives for charging electric vehicles?
Many governments offer incentives such as tax breaks, rebates, and subsidies to encourage electric vehicle adoption. Check with your local authorities to see what incentives are available in your region.
What are the future trends in electric vehicle charging costs?
Future trends in electric vehicle charging costs are expected to be influenced by factors such as advancements in battery technology, increased competition in the charging infrastructure market, and government policies. The cost of charging is likely to decrease as technology improves and infrastructure expands.






