What is the most dramatic solar strom called – What’s the most dramatic solar storm called? The answer lies in a cataclysmic event known as the Carrington Event, a solar storm of unprecedented magnitude that occurred in 1859. This event, named after the British astronomer Richard Carrington who witnessed it, unleashed a torrent of energy from the sun, impacting Earth in ways never seen before. Imagine a world where telegraphs spark and catch fire, auroras illuminate the skies even at the equator, and the very fabric of our technological infrastructure is threatened.
The Carrington Event serves as a stark reminder of the immense power of the sun and the potential consequences of its violent outbursts.
Solar storms are a natural phenomenon, arising from the sun’s dynamic activity. These eruptions of energy and charged particles can travel through space, sometimes reaching Earth and disrupting our technological systems. While most solar storms are relatively minor, some, like the Carrington Event, can have devastating effects. Understanding these events is crucial for safeguarding our technological infrastructure and ensuring the continuity of our modern way of life.
Introduction to Solar Storms
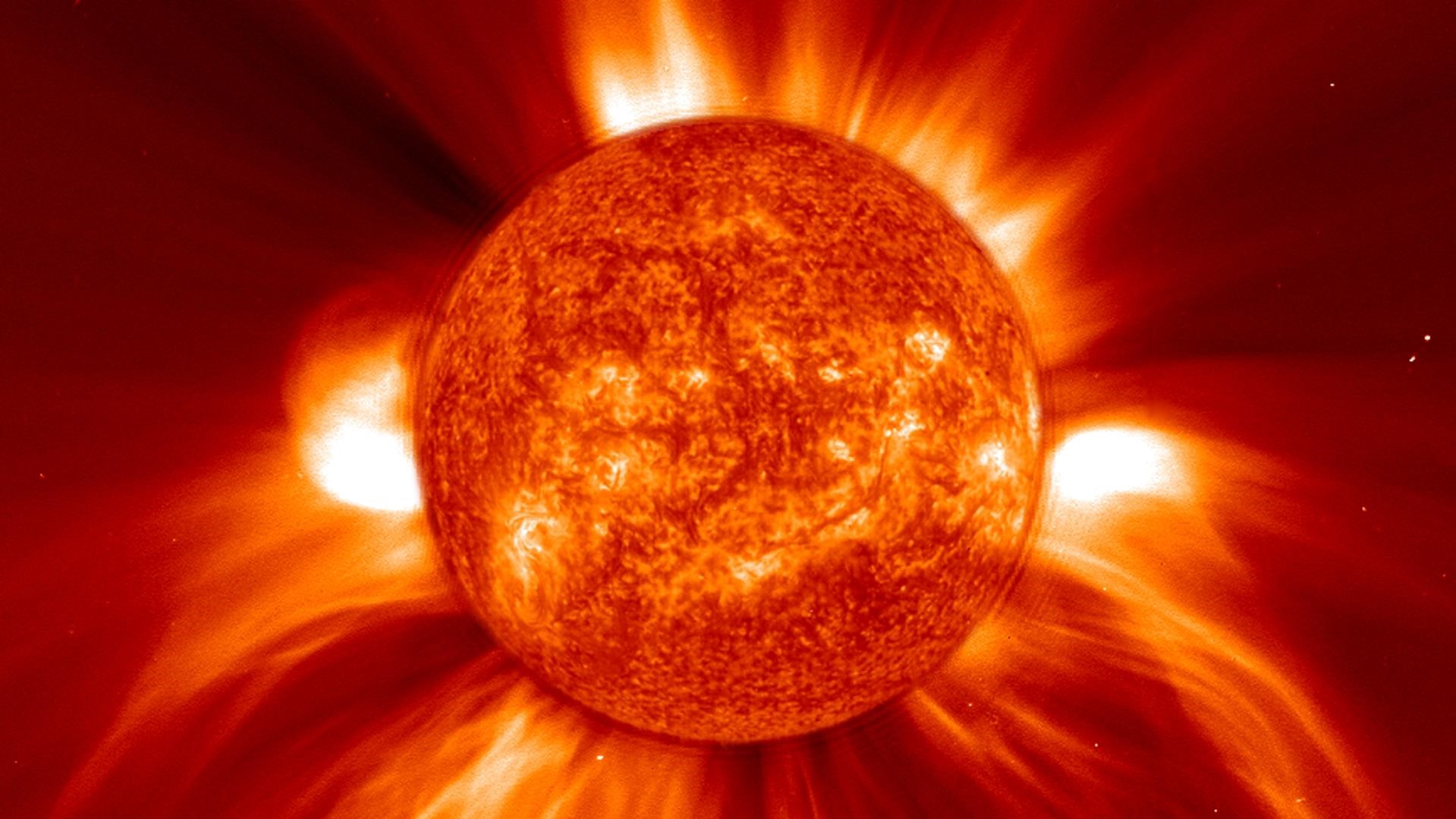
Our Sun, the source of life on Earth, is also a powerful force capable of unleashing massive bursts of energy known as solar storms. These storms can have significant impacts on our planet, ranging from disrupting communication systems to causing widespread power outages. Solar storms are caused by sudden releases of energy from the Sun’s atmosphere, known as the corona.
These releases can occur in various forms, each with its own characteristics and potential effects.
Types of Solar Storms
Solar storms can be categorized into different types based on the specific phenomena they involve:
- Solar Flares: These are sudden bursts of intense energy that release X-rays and ultraviolet radiation. Solar flares can heat the Sun’s atmosphere to millions of degrees Celsius and accelerate charged particles to near-light speeds.
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs): These are giant clouds of plasma and magnetic field lines that erupt from the Sun’s corona. CMEs can travel at speeds of hundreds of kilometers per second, carrying billions of tons of matter.
- Solar Energetic Particle Events (SEPs): These events involve high-energy particles, primarily protons, accelerated by solar flares or CMEs. SEPs can pose a radiation hazard to astronauts and satellites.
Impacts of Solar Storms on Earth, What is the most dramatic solar strom called
Solar storms can have a range of impacts on Earth, depending on their intensity and the direction of the eruption.
- Disruption of Communication Systems: Solar storms can disrupt radio communication, GPS navigation, and satellite operations. Charged particles from solar storms can interfere with radio waves, causing signal degradation or blackouts.
- Power Grid Outages: Large-scale solar storms can induce powerful electric currents in power grids, potentially causing transformers to overheat and fail. The 1989 Quebec blackout, which affected millions of people, was caused by a solar storm.
- Radiation Hazard: High-energy particles from solar storms can pose a radiation hazard to astronauts in space and even to passengers on high-altitude flights.
- Auroras: When charged particles from solar storms interact with Earth’s magnetic field, they can create spectacular displays of light in the sky known as auroras. These auroras are typically observed in the polar regions, but intense solar storms can cause them to appear at lower latitudes.
Space Weather Monitoring and Prediction: What Is The Most Dramatic Solar Strom Called
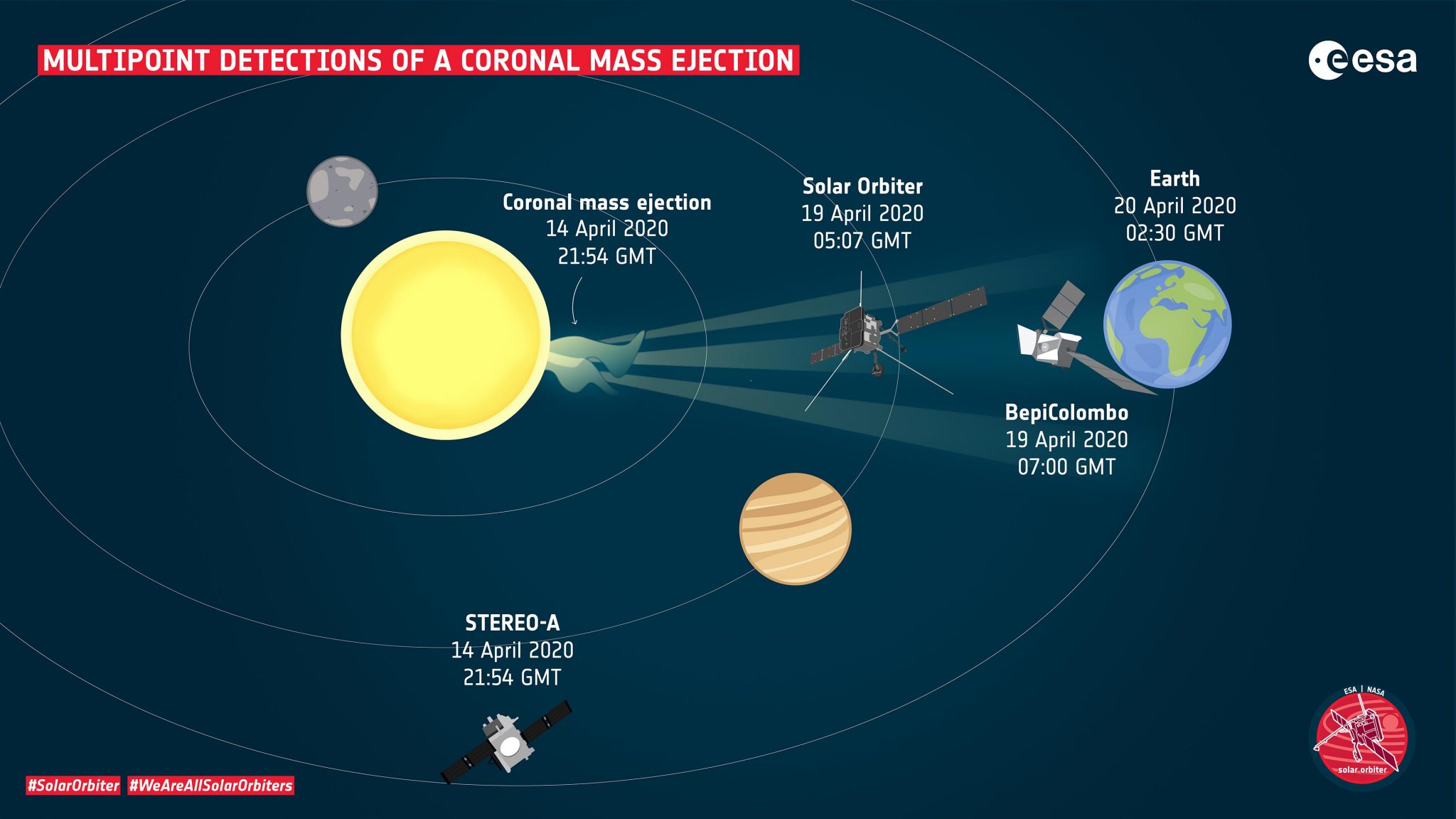
Space weather forecasting plays a crucial role in mitigating the risks associated with solar storms. By providing timely warnings and predictions, it allows for proactive measures to protect critical infrastructure, satellites, and astronauts.
Technologies Used for Monitoring and Prediction
Space weather forecasting relies on a network of ground-based and space-borne instruments to monitor and predict solar activity. These technologies provide continuous data on various aspects of the Sun, enabling scientists to track and anticipate potential threats.
- Solar Observatories: Ground-based observatories, such as the National Solar Observatory (NSO) in the United States, use sophisticated telescopes to observe the Sun’s surface and atmosphere. These observatories capture images and gather data on solar flares, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and other phenomena that can influence space weather.
- Spacecraft: Spacecraft, like the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), orbit the Sun and provide continuous observations of its activity. They capture high-resolution images and measure the Sun’s magnetic field, radiation, and particle emissions.
- Ground-Based Sensors: Ground-based sensors, such as magnetometers and ionosondes, monitor the Earth’s magnetic field and ionosphere, which are directly affected by solar storms. These sensors provide real-time data on the intensity and direction of geomagnetic disturbances.
Challenges and Limitations of Space Weather Forecasting
Despite advancements in technology, space weather forecasting still faces significant challenges and limitations.
- Predicting the Timing and Intensity of Solar Storms: Predicting the exact timing and intensity of solar storms remains a challenge. While scientists can monitor solar activity and identify potential threats, accurately predicting their impact on Earth is complex and requires sophisticated models.
- Limited Data Availability: The limited availability of real-time data from all regions of the Sun can hinder accurate predictions. Spacecraft and ground-based instruments provide valuable data, but their coverage is not comprehensive.
- Complexity of Solar Processes: Solar processes are complex and not fully understood. The interaction of magnetic fields, plasma, and radiation within the Sun can lead to unpredictable events that can significantly impact space weather.
The Carrington Event serves as a wake-up call, reminding us of the sun’s immense power and the vulnerability of our technological infrastructure to its unpredictable outbursts. While we have made significant strides in understanding and monitoring space weather, predicting and mitigating the impact of severe solar storms remains a complex challenge. As we continue to rely on technology that is susceptible to these events, it becomes increasingly vital to invest in robust space weather forecasting and mitigation strategies.
By doing so, we can ensure that our technological advancements are not left at the mercy of the sun’s unpredictable moods.
Essential Questionnaire
What causes solar storms?
Solar storms are caused by eruptions of energy and charged particles from the sun’s surface, often associated with sunspots and solar flares.
How often do solar storms occur?
Solar storms occur regularly, with varying intensity and frequency. Some are minor, while others can be more significant.
Are solar storms dangerous to humans?
While most solar storms pose no direct threat to humans on Earth’s surface, they can disrupt satellites and communication systems, potentially leading to power outages and other disruptions.
Can we predict solar storms?
Scientists can monitor solar activity and predict the likelihood of solar storms, but predicting their exact timing and intensity remains challenging.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/common-house-spiders-2656509_V2-a9c74187a3944f3a85d19437953cf17a.png?w=700)