Which is most secure psk radius pki – Which PSK, RADIUS, or PKI is most secure? This question is a critical one for network administrators seeking to bolster their security posture. Each authentication method offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, impacting the overall security of your network infrastructure.
This article delves into the intricacies of each method, exploring their strengths and weaknesses, and ultimately providing guidance on choosing the most suitable option for your specific needs. We’ll cover key aspects like authentication strength, key management, access control, and vulnerability mitigation, providing a comprehensive understanding of these authentication protocols.
Network Authentication: Choosing the Right Method
Yo, network security is like the foundation of any digital world, and authentication is the lock on the door. It’s about making sure only the right people get in, like, you don’t want just anyone strolling into your server room, right? There are a bunch of different ways to do this, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. We’re gonna break down three of the most popular methods: PSK, RADIUS, and PKI, and see which one is the most secure.
PSK Authentication
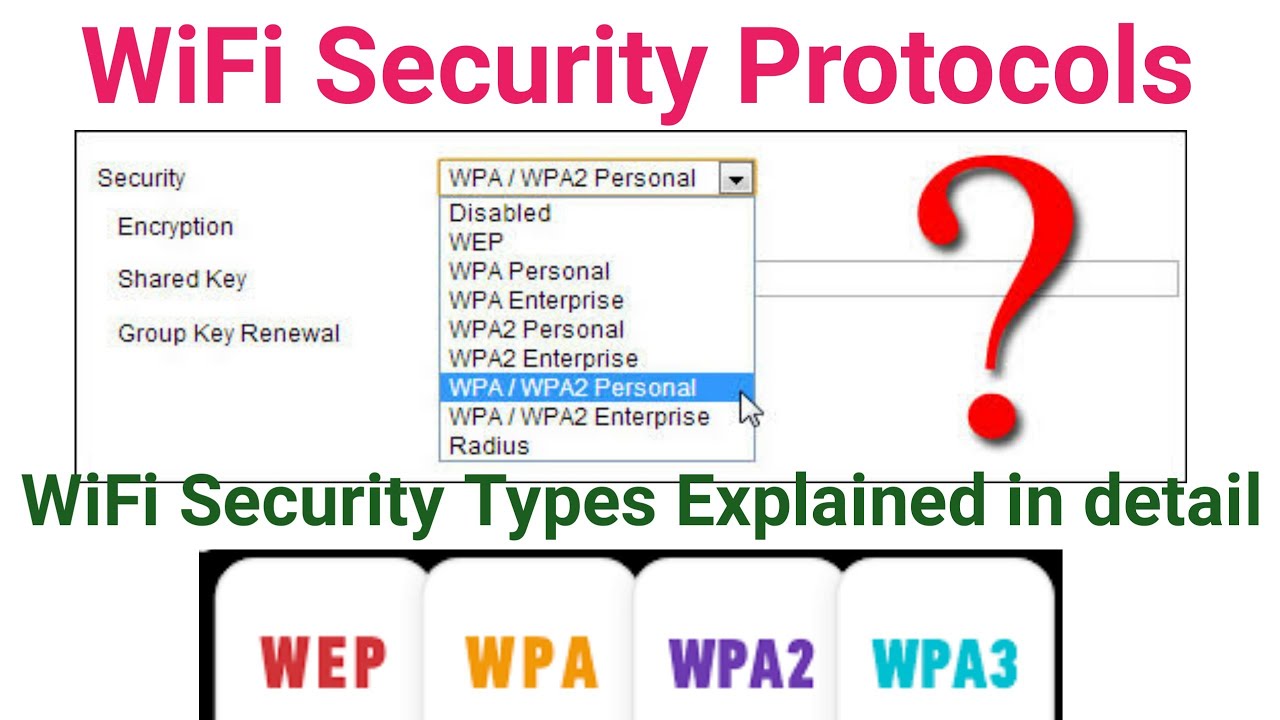
PSK, or Pre-Shared Key, is like a secret handshake. You have a key, the other device has the same key, and if you both match, you’re good to go. It’s super simple, but it’s also super vulnerable. Think of it like having the same password for every account – if someone gets your key, they can access everything.
PSK (Pre-Shared Key) Authentication
+with+either.jpg)
PSK authentication is a simple and cost-effective method of securing network access. It relies on a shared secret key, known as a Pre-Shared Key (PSK), which is used to authenticate devices to a network.
PSK Authentication Process, Which is most secure psk radius pki
The PSK authentication process involves several steps:
- Key Generation: A unique PSK is generated for each network. This key should be a strong, random string of characters, typically 32 to 64 characters long.
- Key Distribution: The PSK must be securely distributed to all devices that need to access the network. This can be done manually, using a configuration file, or through a secure channel.
- Authentication: When a device attempts to connect to the network, it presents its PSK to the access point or network device.
- Verification: The access point or network device verifies the PSK against the stored key. If the keys match, the device is authenticated and granted access to the network.
Advantages of PSK Authentication
PSK authentication offers several advantages:
- Simplicity: It is relatively easy to implement and configure.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It does not require any additional infrastructure or certificates.
- Flexibility: It can be used with various network protocols, such as WPA2/3 and 802.1x.
Security Vulnerabilities of PSK Authentication
While PSK authentication is simple and cost-effective, it has several security vulnerabilities:
- Key Compromise: If the PSK is compromised, attackers can gain unauthorized access to the network. This can happen through various methods, such as phishing attacks, social engineering, or brute-force attacks.
- Brute-Force Attacks: Attackers can attempt to guess the PSK by trying different combinations of characters. This can be mitigated by using a strong, random PSK and limiting the number of authentication attempts.
- Key Management: Managing and distributing PSKs securely can be challenging, especially in large networks.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) Authentication
Yo, so RADIUS is like the bouncer at a club, checking IDs and making sure only the cool peeps get in. It’s a network protocol that handles user authentication and authorization for network access. Think of it as the middleman between your devices and the network, making sure everything’s legit.
RADIUS Authentication Process
Alright, let’s break down how this whole RADIUS thing works. Imagine you’re trying to log in to your school’s Wi-Fi. Your device, the client, sends a request to the RADIUS server, like the school’s network admin. This request includes your username and password. The RADIUS server then checks your credentials against its database.
If everything checks out, it sends a response back to your device, granting you access to the network. If your credentials are bogus, the server tells your device to bounce, no Wi-Fi for you!
Shared Secrets and Encryption
Now, RADIUS uses shared secrets and encryption to keep things secure. It’s like a secret handshake between the client and the server. They both have the same secret key, which is used to encrypt the communication between them. This prevents eavesdroppers from snooping on your login info. Think of it like a secret code that only you and the server know, making sure nobody else can understand your conversation.
Advantages of RADIUS
Yo, RADIUS has some serious perks, making it a popular choice for network authentication:
- Centralized Authentication: RADIUS allows you to manage all your users and their permissions from a single server. This makes it easy to add new users, update passwords, and control access to different network resources. Think of it like having one place to manage all your friends’ info, instead of keeping separate lists for each party you go to.
- Scalability: RADIUS can handle a large number of users and devices. It’s like a club that can accommodate a huge crowd without missing a beat. As your network grows, RADIUS can easily scale to handle the increased traffic.
- Flexibility: RADIUS can be used for various authentication methods, like username/password, digital certificates, and even two-factor authentication. It’s like having a versatile bouncer who can check different types of IDs.
Security Concerns with RADIUS
While RADIUS is pretty secure, it’s not invincible. Here are some potential vulnerabilities to keep in mind:
- Weak Passwords: If users choose weak passwords, it’s easy for hackers to guess them and gain unauthorized access. It’s like having a flimsy lock on your door that anyone can pick.
- Server Vulnerabilities: RADIUS servers can be targeted by hackers who try to exploit vulnerabilities in the server software. Think of it like a burglar trying to break into your network’s security system.
- Replay Attacks: Hackers can try to replay previously recorded RADIUS messages to gain unauthorized access. It’s like using a fake ID that looks exactly like the real one. RADIUS can be configured to prevent replay attacks using techniques like timestamps and sequence numbers.
PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) Authentication
PKI authentication is a robust method that uses digital certificates and asymmetric cryptography to verify identities and secure communication. This approach goes beyond simple passwords, offering a more secure and reliable way to authenticate users and devices.
Certificate Generation, Signing, and Validation
PKI relies on digital certificates, which are electronic documents that bind a public key to an entity, such as a user, device, or server. These certificates are issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) and are used to verify the authenticity and integrity of the entity. The process of generating, signing, and validating certificates is crucial for establishing trust and ensuring secure communication.
- Certificate Generation: When an entity needs a certificate, it submits a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) to a CA. The CSR contains information about the entity, including its name, organization, and public key. The CA verifies the information and generates a digital certificate that includes the entity’s public key, a unique serial number, the CA’s digital signature, and other relevant details.
- Certificate Signing: The CA digitally signs the certificate using its private key. This signature ensures the certificate’s authenticity and integrity, guaranteeing that it has not been tampered with. The CA’s public key is widely trusted, allowing recipients to verify the signature.
- Certificate Validation: When an entity receives a certificate, it can validate its authenticity and integrity by verifying the CA’s digital signature. The entity’s software or browser uses the CA’s public key to decrypt the signature and confirm that the certificate is valid and issued by a trusted authority.
Asymmetric Cryptography and Digital Signatures
PKI authentication utilizes asymmetric cryptography, which involves a pair of mathematically related keys: a public key and a private key. The public key can be shared with anyone, while the private key must be kept secret.
- Public Key: Used for encrypting data or verifying digital signatures. Anyone can use the public key to encrypt data or verify a signature.
- Private Key: Used for decrypting data or signing digital certificates. Only the owner of the private key can decrypt data encrypted with the corresponding public key or sign a digital certificate.
Digital signatures are created using the private key and are used to ensure the authenticity and integrity of electronic documents. When an entity signs a document, it uses its private key to generate a unique digital signature that is attached to the document. The recipient can then use the sender’s public key to verify the signature and ensure that the document has not been tampered with.
Advantages of PKI Authentication
PKI authentication offers numerous advantages over traditional authentication methods, such as password-based systems:
- Strong Authentication: PKI provides strong authentication by verifying the identity of the entity using digital certificates and public key cryptography. This ensures that only authorized individuals or devices can access sensitive information.
- Non-Repudiation: Digital signatures provide non-repudiation, meaning that a sender cannot deny having sent a message or document. The signature proves that the sender was the one who created the message or document, making it impossible for them to deny their actions.
- Secure Communication: PKI can be used to encrypt communications, ensuring that only the intended recipient can read the message. This protects sensitive information from unauthorized access during transmission.
- Scalability: PKI can be easily scaled to accommodate large numbers of users and devices. It is also flexible and can be used in various applications, including email, web browsing, and network access.
Security Vulnerabilities Associated with PKI
While PKI offers significant security benefits, it is not without its vulnerabilities. It’s important to be aware of potential threats and implement appropriate security measures:
- Certificate Revocation: When a certificate is compromised or no longer valid, it needs to be revoked to prevent its misuse. The revocation process involves updating the Certificate Revocation List (CRL) or using Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) to inform users and systems about revoked certificates. However, delays in revocation can lead to security risks.
- Key Compromise: If a private key is compromised, an attacker can impersonate the entity associated with that key. This can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information and systems. Strong key management practices, such as using hardware security modules (HSMs) to store private keys, are essential to prevent key compromise.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Attackers can attempt to intercept communication and impersonate the CA, issuing fraudulent certificates. This can lead to the installation of malicious software or the theft of sensitive information. Using trusted CAs and verifying certificates carefully is crucial to mitigate this threat.
- Certificate Expiration: Certificates have a limited lifespan, and they need to be renewed before they expire. If a certificate expires, it will no longer be valid, and communication using that certificate will fail. Regular monitoring and renewal of certificates are essential to maintain continuous security.
Comparison of Security Features
Yo, let’s break down the security of PSK, RADIUS, and PKI. These authentication methods are like the security guards of your network, but each one has its own strengths and weaknesses.
Security Features Comparison
Alright, so we’re gonna compare PSK, RADIUS, and PKI based on their security features. We’ll use a table to make it easier to see the differences.
| Feature | PSK | RADIUS | PKI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authentication Strength | Strong if the key is kept secret, but vulnerable to brute-force attacks. | Strong if the RADIUS server is secure, but vulnerable to attacks on the RADIUS protocol. | Very strong, but requires complex infrastructure and key management. |
| Key Management | Simple, but requires manual distribution and storage of the key. | More complex, requiring a centralized RADIUS server to manage keys. | Very complex, requiring a hierarchical system of certificates and keys. |
| Access Control | Limited, as the same key is used for all users. | Flexible, allowing for different access rights for different users. | Very flexible, allowing for granular access control based on user roles and permissions. |
| Vulnerability Mitigation | Vulnerable to brute-force attacks and key compromise. | Vulnerable to attacks on the RADIUS protocol and server compromise. | Vulnerable to certificate compromise and attacks on the PKI infrastructure. |
Best Practices for Secure Authentication: Which Is Most Secure Psk Radius Pki
Yo, so we’ve been talkin’ about PSK, RADIUS, and PKI, but it’s all about how to keep your network safe, right? Let’s get into some best practices to make sure you’re using the right tools and methods for your specific situation.
Choosing the Right Authentication Method
Choosing the right authentication method is like picking the right outfit for a party—you gotta know what’s gonna work best for the situation. Think about your network’s needs:* Size and complexity: A small network might be fine with PSK, but a larger, more complex network might need RADIUS or PKI for better management and security.
Security requirements
If you’re dealing with sensitive data, PKI is probably the way to go because it offers the highest level of security.
Budget
PKI can be more expensive to implement and maintain, so you gotta consider your budget when making your choice.
Best Practices for Implementing and Managing Authentication Systems
Now that you’ve picked your method, let’s talk about how to set it up and keep it running smoothly:* Strong passwords: This is like the foundation of your network security. Use strong passwords, with a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
Regular password changes
Change your passwords regularly to reduce the risk of someone cracking them.
Two-factor authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to provide two pieces of information—like a password and a code from your phone—before you can log in.
Access control
Limit access to sensitive data and resources to only authorized users.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments
Think of these like check-ups for your network. They help you identify and fix security flaws before they can be exploited.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Yo, these are like your network’s annual physicals. They’re essential for keeping your network safe:* Identify vulnerabilities: Audits and assessments can help you spot weaknesses in your network’s security.
Prevent attacks
By identifying vulnerabilities, you can patch them before they’re exploited by attackers.
Stay compliant
Many industries have regulations that require regular security audits.
Future Trends in Network Authentication
The world of network security is constantly evolving, and authentication methods are no exception. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the need for robust and adaptable authentication solutions is paramount. Emerging technologies and evolving security landscapes are driving significant changes in how we authenticate users and devices.
The Rise of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a critical component of enhancing network security, and its importance is only growing. By requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Biometric Authentication: This method uses unique biological traits, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, to verify identity. Biometric authentication is becoming increasingly prevalent, especially in mobile devices and access control systems.
- Behavioral Analytics: This approach analyzes user behavior patterns, such as typing speed, mouse movements, and device usage, to detect anomalies that could indicate unauthorized access. Behavioral analytics can be used to supplement traditional MFA methods and provide an additional layer of security.
- Contextual Authentication: This method considers the user’s location, device type, and time of day to determine the appropriate level of authentication. For example, accessing a sensitive system from a new location might require a stronger authentication method than accessing the same system from a known and trusted location.
The Future of PSK, RADIUS, and PKI Authentication
While traditional authentication methods like PSK, RADIUS, and PKI remain valuable, they are constantly being refined and adapted to address evolving security threats.
- PSK (Pre-Shared Key): PSK authentication is often used in small-scale networks or for initial device provisioning. However, its reliance on a single shared secret makes it vulnerable to attacks if the secret is compromised. To enhance PSK security, techniques like key rotation and secure storage are being implemented.
- RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service): RADIUS is widely used for centralized authentication and authorization in large networks. Its strength lies in its scalability and flexibility, but it can be susceptible to attacks if not properly configured and secured. Future trends in RADIUS authentication include the adoption of more robust encryption protocols and the integration of MFA for enhanced security.
- PKI (Public Key Infrastructure): PKI offers strong authentication and encryption capabilities through digital certificates. However, managing and maintaining a PKI infrastructure can be complex and resource-intensive. Future trends in PKI authentication focus on simplifying certificate management, reducing the burden on administrators, and exploring the use of blockchain technology to enhance security and trust.
Ultimately, the choice of the most secure authentication method depends on your specific network requirements, budget, and risk tolerance. By understanding the nuances of PSK, RADIUS, and PKI, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your security goals. Remember, a robust security strategy requires ongoing monitoring, regular security audits, and proactive vulnerability assessments to ensure the ongoing protection of your network.
Essential FAQs
What are the main differences between PSK, RADIUS, and PKI?
PSK relies on a shared secret key, RADIUS uses a centralized server with shared secrets, and PKI employs digital certificates and asymmetric cryptography.
Can I use multiple authentication methods simultaneously?
Yes, you can implement a multi-factor authentication (MFA) strategy by combining different methods, such as PKI for initial authentication and RADIUS for subsequent access control.
What are some common security best practices for authentication?
Use strong passwords, implement multi-factor authentication, regularly update software and firmware, and conduct regular security audits.






