What is secure processing center – Ever heard of a Secure Processing Center (SPC)? Basically, it’s like a super-secure vault for your data, but way more complex. Think of it as a digital fortress where your sensitive information is locked down tight, guarded by a whole army of security measures.
SPCs are super important for industries that handle super-sensitive data like financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies. They make sure that your data is protected from hackers, natural disasters, and even accidental leaks. It’s all about keeping your information safe and sound.
Definition and Purpose
A Secure Processing Center (SPC) is a highly controlled and secure environment designed to handle sensitive data and critical operations. It’s like a fortress for information, built to protect it from unauthorized access, physical threats, and cyberattacks.The primary purpose of an SPC is to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of sensitive data. It provides a safe and reliable platform for processing, storing, and managing information that requires a high level of security.
Industries and Organizations Utilizing SPCs
SPCs are commonly used in various industries and organizations that handle sensitive data, including:
- Financial institutions: Banks, credit card companies, and investment firms use SPCs to protect financial transactions, customer data, and other sensitive information.
- Government agencies: Government agencies, such as intelligence agencies, law enforcement, and military organizations, rely on SPCs to safeguard classified information and national security.
- Healthcare organizations: Hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies use SPCs to protect patient records, medical data, and other sensitive health information.
- Technology companies: Tech companies, especially those dealing with cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data analytics, use SPCs to protect their infrastructure and customer data.
Security Measures and Features

A Secure Processing Center (SPC) employs a multi-layered security approach to safeguard sensitive data and critical operations. These measures are designed to mitigate risks from various threats, including physical intrusions, cyberattacks, and internal security breaches. The security measures encompass both physical and logical controls, ensuring a comprehensive and robust security posture.
Physical Security Measures
Physical security measures focus on securing the physical environment of the SPC and controlling access to its facilities. These measures aim to deter unauthorized entry and prevent physical damage to equipment and data.
- Access Control: The SPC utilizes a multi-factor authentication system for entry, requiring individuals to present valid identification and undergo biometric verification. This system restricts access to authorized personnel and maintains a record of all entry and exit activities.
- Surveillance: The SPC is equipped with a comprehensive surveillance system, including closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras, motion detectors, and intrusion alarms. These systems monitor the perimeter and interior of the facility, detecting any suspicious activity and providing visual evidence in case of an incident.
- Environmental Controls: To protect against environmental hazards, the SPC employs environmental control systems, including fire suppression systems, temperature and humidity controls, and backup power generators. These systems maintain a safe and stable operating environment for critical infrastructure and equipment.
Logical Security Measures
Logical security measures focus on securing the SPC’s IT infrastructure and data. These measures aim to prevent unauthorized access to systems and data, protect against cyberattacks, and ensure data integrity.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between the SPC’s internal network and the external internet, blocking unauthorized access and preventing malicious traffic from entering the network. Firewalls analyze incoming and outgoing network traffic, filtering out suspicious activity based on predefined rules and policies.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns and activities, alerting security personnel to potential threats. IDS use various techniques, including signature-based detection and anomaly detection, to identify and respond to potential intrusions.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption protects sensitive information by transforming it into an unreadable format. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be accessed or understood without the appropriate decryption key. Encryption is applied to data at rest and in transit, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
Data Processing and Handling
Secure Processing Centers (SPCs) are designed to handle sensitive data with utmost care and security. The types of data processed within an SPC vary depending on the specific industry and purpose, but generally include personal information, financial records, medical data, and other confidential details. These centers employ rigorous procedures for data storage, retrieval, and management to ensure data integrity and compliance with relevant regulations.
Data Storage and Retrieval
Data storage within an SPC is typically conducted using secure, redundant systems. These systems are designed to minimize the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or natural disasters. Data is often stored in multiple locations, with backups regularly created and stored off-site.
- Data Encryption: Data is encrypted both at rest and in transit, meaning it is scrambled before being stored and remains encrypted during transmission. This ensures that even if unauthorized access is gained, the data remains unintelligible.
- Access Control: Access to data is strictly controlled through multi-factor authentication and role-based access control. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific data sets, minimizing the risk of unauthorized data access.
- Data Auditing: Regular audits are conducted to ensure that data is stored and accessed securely. These audits track all data access events, including user identity, time of access, and data accessed. This provides a comprehensive audit trail for compliance and security purposes.
Data Integrity and Compliance
Data integrity is paramount within an SPC. Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of data is critical for maintaining trust and complying with relevant regulations.
- Data Validation: Data is rigorously validated to ensure accuracy and consistency. This includes verifying data formats, checking for duplicates, and ensuring data adheres to predefined rules.
- Data Governance: A robust data governance framework is implemented to establish clear ownership, responsibilities, and processes for managing data. This framework ensures data quality, security, and compliance.
- Compliance with Regulations: SPCs operate in compliance with relevant regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). These regulations dictate how sensitive data must be handled, stored, and protected.
Compliance and Certifications
Secure Processing Centers (SPCs) are subject to a range of compliance requirements and industry standards, ensuring the protection and integrity of sensitive data. These standards serve as frameworks for data security, privacy, and operational excellence, fostering trust and confidence in the SPC’s ability to handle sensitive information responsibly.
Industry Standards and Compliance Requirements
Industry standards and compliance requirements are crucial for SPCs to demonstrate their commitment to data security and privacy. They provide a framework for implementing robust security measures and adhering to best practices.
- ISO 27001: This international standard focuses on information security management systems (ISMS), providing a comprehensive framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an organization’s information security. SPCs adhering to ISO 27001 demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding sensitive data through a structured approach to risk management, policy development, and security controls.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): This standard mandates specific security requirements for organizations that process, store, or transmit cardholder data. SPCs handling payment card information must comply with PCI DSS to protect cardholders from fraud and data breaches. This standard focuses on areas such as network security, access control, data encryption, and vulnerability management.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): This US federal law protects the privacy and security of protected health information (PHI). SPCs handling healthcare data must comply with HIPAA regulations to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI. This involves implementing policies and procedures for data access control, encryption, and breach notification.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This European Union regulation protects the personal data of individuals within the EU. SPCs processing personal data of EU residents must comply with GDPR principles, including data minimization, purpose limitation, and data subject rights.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: This framework, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), provides a voluntary set of guidelines for improving cybersecurity practices. SPCs can leverage the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to assess their current security posture, identify gaps, and implement appropriate controls to mitigate risks.
Significance of Certifications
Certifications like ISO 27001 and PCI DSS provide independent verification that an SPC meets specific security standards. These certifications are highly valued by customers and stakeholders, demonstrating the SPC’s commitment to data security and compliance.
- Enhanced Trust and Credibility: Certifications instill confidence in customers and partners, demonstrating that the SPC has met rigorous security standards and is committed to protecting sensitive information. This can be particularly crucial for organizations handling sensitive data, such as financial records, healthcare information, or personal data.
- Reduced Risk and Liability: Compliance with industry standards and certifications can help SPCs mitigate risks and reduce liability in case of data breaches or security incidents. These standards provide a framework for implementing robust security controls, reducing the likelihood of data compromise and potential legal repercussions.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Certifications often require organizations to implement specific security practices and procedures, which can streamline operations and improve overall efficiency. This includes processes for risk management, incident response, and security awareness training, contributing to a more secure and efficient data processing environment.
- Competitive Advantage: Achieving certifications can differentiate SPCs from competitors, showcasing their commitment to data security and compliance. This can be a significant factor for organizations seeking a trusted and reliable partner for data processing services.
Benefits of Compliance and Certification
Achieving compliance and certification for an SPC offers numerous benefits, including enhanced trust, reduced risk, and improved operational efficiency.
- Improved Data Security: Compliance with industry standards and certifications ensures that SPCs implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
- Enhanced Privacy Protection: Compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA protects the privacy of individuals by ensuring that personal data is processed lawfully and securely. This includes measures for data minimization, purpose limitation, and data subject rights.
- Increased Customer Confidence: Certifications demonstrate an SPC’s commitment to data security and privacy, building trust with customers and stakeholders. This can be particularly important for organizations handling sensitive data, as it assures them that their information is being handled responsibly and securely.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: Compliance with industry standards and certifications helps SPCs mitigate risks and reduce the likelihood of data breaches. This includes implementing security controls such as access control, encryption, and vulnerability management.
- Improved Reputation and Brand Value: Achieving compliance and certification can enhance an SPC’s reputation and brand value, showcasing its commitment to data security and ethical practices. This can attract new customers and partners, strengthening the organization’s position in the market.
Benefits and Advantages: What Is Secure Processing Center
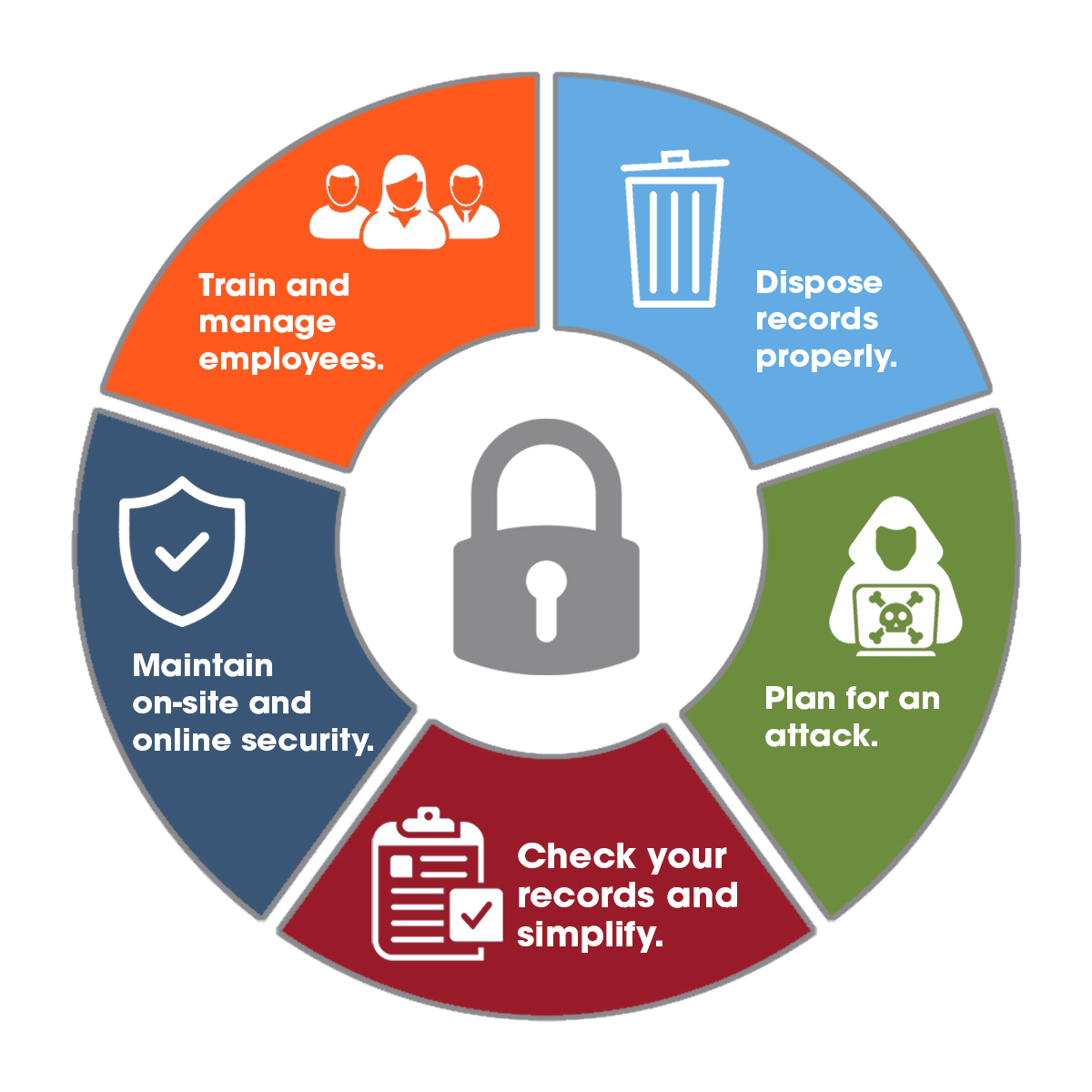
Secure Processing Centers (SPCs) offer a multitude of advantages for organizations seeking to enhance data security, reliability, and operational efficiency. By leveraging the robust infrastructure and comprehensive security measures of SPCs, businesses can gain a significant edge in today’s data-driven landscape.
Enhanced Security and Reliability
SPCs provide a fortified environment for data processing and storage, minimizing the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security threats. The stringent security measures implemented within SPCs, such as physical security, access control, and data encryption, ensure the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
- Physical Security: SPCs employ robust physical security measures, including 24/7 surveillance, controlled access points, and secure perimeter fencing, to deter unauthorized entry and protect against physical threats.
- Access Control: Strict access control policies and procedures are enforced, limiting access to authorized personnel and ensuring that only individuals with appropriate clearance can access sensitive data.
- Data Encryption: Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties and protecting it from potential breaches.
- Redundancy and Disaster Recovery: SPCs typically have redundant systems and backup facilities to ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster or outage.
Improved Business Operations and Reduced Risks, What is secure processing center
The advantages of SPCs extend beyond security, offering tangible benefits that streamline business operations, mitigate risks, and enhance overall efficiency.
- Scalability and Flexibility: SPCs provide scalable infrastructure, allowing businesses to adjust their processing capacity as their data volumes and processing needs evolve. This flexibility ensures that organizations can handle fluctuating workloads without compromising performance.
- Cost Optimization: By outsourcing data processing and storage to an SPC, businesses can reduce capital expenditures on hardware and software, as well as the ongoing costs of maintenance and staff.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: SPCs are often equipped with robust compliance frameworks and certifications, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001, ensuring that businesses meet regulatory requirements and maintain data privacy.
- Reduced Operational Risks: SPCs offer comprehensive security measures, including disaster recovery plans, reducing the risk of data loss, system downtime, and other operational disruptions.
Challenges and Considerations

Implementing and maintaining a Secure Processing Center (SPC) comes with inherent challenges. These challenges encompass a wide range of aspects, from the initial setup to ongoing operations. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and security of the SPC.
Cost and Complexity of Establishing a Secure Processing Environment
The cost of establishing a secure processing environment can be significant, depending on the scale and scope of the operation. The cost factors include infrastructure, hardware, software, security measures, personnel, and ongoing maintenance.
- Infrastructure Costs: The physical infrastructure of an SPC, including building space, power supply, network infrastructure, and physical security measures, represents a substantial initial investment.
- Hardware and Software Costs: The SPC requires specialized hardware, such as servers, storage systems, and network devices, as well as robust security software, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption tools.
- Personnel Costs: Maintaining a secure processing environment necessitates skilled personnel, including security experts, data analysts, system administrators, and compliance officers.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: The SPC requires ongoing maintenance, including system updates, security patches, and regular security assessments, to ensure continued security and performance.
In addition to the cost, establishing a secure processing environment involves significant complexities. These complexities include:
- Compliance with Regulations: The SPC must comply with relevant industry regulations and data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
- Security Architecture Design: Designing a robust security architecture requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including network segmentation, access control, data encryption, and incident response procedures.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating the SPC with existing systems and applications requires careful planning and execution to ensure seamless data flow and maintain security.
Ongoing Security Assessments and Vulnerability Management
Ongoing security assessments and vulnerability management are essential for maintaining the security of an SPC. These assessments identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system, enabling proactive mitigation measures.
- Regular Security Assessments: Regular security assessments, conducted by internal teams or external security experts, help identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the SPC’s security posture.
- Vulnerability Management: Vulnerability management involves identifying, prioritizing, and mitigating vulnerabilities in the SPC’s systems and applications. This process includes patch management, security configuration hardening, and vulnerability remediation.
- Penetration Testing: Penetration testing involves simulating real-world attacks to identify security weaknesses and assess the effectiveness of the SPC’s security controls.
So, the next time you hear about a Secure Processing Center, remember it’s more than just a fancy name. It’s a crucial part of keeping your data safe and secure in today’s digital world. It’s like having a personal bodyguard for your information, ensuring that it’s protected from all kinds of threats. And that’s pretty important, right?
Popular Questions
What are some examples of SPCs in action?
Think of a bank’s main data center where all their customer information is stored. That’s an SPC. Or a hospital’s server room that houses patient records. That’s another example.
Why are SPCs so important?
SPCs are vital for preventing data breaches and protecting sensitive information. They’re like the ultimate defense against cybercriminals and other threats.
Are SPCs expensive to set up?
Yes, implementing an SPC can be costly due to the advanced security measures and specialized equipment required. But the cost is justified by the protection it provides for your valuable data.






