How much is 0 food stamps worth in cash – How much is $300 in food stamps worth in cash? This question delves into the practical realities of the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), a vital lifeline for millions of Americans struggling with food insecurity. While $300 may seem like a modest sum, it can significantly impact a household’s ability to access nutritious food.
By examining the purchasing power of SNAP benefits, we can gain a deeper understanding of their role in addressing food insecurity and the challenges faced by low-income families.
The value of $300 in SNAP benefits depends on various factors, including regional food prices, household size, and dietary needs. However, it’s crucial to recognize that SNAP benefits are not equivalent to cash. SNAP recipients can only use their benefits to purchase eligible food items at participating grocery stores.
This limitation, along with the restrictions on non-food items and restaurant meals, highlights the unique nature of SNAP benefits and their distinct role in food assistance.
Understanding SNAP Benefits
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as food stamps, is a federal program designed to help low-income families and individuals purchase nutritious food. SNAP benefits are crucial for many Americans, ensuring access to essential food items and promoting food security.
SNAP Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for SNAP benefits, individuals and households must meet specific criteria related to income, resources, and household size. The eligibility requirements are determined by the federal government but may vary slightly based on state regulations.
Income Requirements
SNAP eligibility is based on a household’s gross income, which includes all sources of income before taxes and deductions. Households must have a gross income that is below the SNAP income limits, which are adjusted annually based on household size and state cost of living.
Resource Requirements
SNAP recipients also have limits on the amount of resources they can possess. These resources include assets like cash, savings, and vehicles. The resource limits are based on household size and are intended to ensure that individuals receiving SNAP benefits are truly in need.
Other Eligibility Criteria
Besides income and resource limits, there are other eligibility criteria for SNAP benefits. For instance, most applicants must be U.S. citizens or legal residents, and some states may have additional requirements, such as work registration or proof of residency.
Average SNAP Benefit Amount, How much is 0 food stamps worth in cash
The average monthly SNAP benefit amount varies depending on factors such as household size, state, and individual circumstances. In 2023, the average monthly SNAP benefit across the United States was approximately $156. However, it’s important to note that this is just an average, and individual benefit amounts can range significantly.
$300 SNAP Benefit in Context

$300 in SNAP benefits can be a valuable resource for individuals and families to purchase groceries, helping them access nutritious food and maintain a healthy diet. However, understanding the limitations and nuances of SNAP benefits is crucial to make the most of this program.
Breakdown of $300 SNAP Benefit for Grocery Purchases
$300 in SNAP benefits can be used to purchase a variety of groceries, including fruits, vegetables, dairy products, meat, poultry, fish, bread, cereal, and other staple items. The specific items that can be purchased with SNAP benefits are subject to the USDA’s Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) guidelines.
- Fruits and Vegetables:A significant portion of the SNAP budget can be allocated to fresh produce, providing essential vitamins and minerals. Examples include apples, bananas, oranges, potatoes, carrots, onions, and leafy greens.
- Dairy Products:Milk, yogurt, and cheese are essential sources of calcium and protein. SNAP benefits can be used to purchase these items, contributing to a balanced diet.
- Protein Sources:Meat, poultry, fish, beans, and lentils are excellent sources of protein, which is vital for muscle growth and repair. SNAP benefits can be used to purchase these items, ensuring adequate protein intake.
- Grains:Bread, cereal, rice, and pasta are staple foods that provide carbohydrates for energy. SNAP benefits can be used to purchase these items, ensuring a consistent source of energy.
- Other Staple Items:SNAP benefits can also be used to purchase other essential items, such as eggs, cooking oil, and canned goods. These items provide additional nutrients and can be used in various meals.
Sample Grocery Shopping List Using $300 SNAP Benefit
A sample grocery shopping list using $300 in SNAP benefits can be structured as follows:
- Fruits and Vegetables:$50 (apples, bananas, oranges, potatoes, carrots, onions, lettuce)
- Dairy Products:$30 (milk, yogurt, cheese)
- Protein Sources:$70 (chicken breasts, ground beef, beans, lentils)
- Grains:$40 (bread, cereal, rice, pasta)
- Other Staple Items:$30 (eggs, cooking oil, canned tomatoes, canned beans)
- Frozen Foods:$30 (frozen vegetables, frozen fruit, frozen meals)
- Snacks:$20 (trail mix, granola bars, dried fruit)
Comparison of $300 SNAP Benefit to $300 in Cash
While $300 in SNAP benefits can be used to purchase a significant amount of groceries, it is important to note that the purchasing power of SNAP benefits is generally lower than $300 in cash. This is because SNAP benefits can only be used to purchase eligible food items, while cash can be used for a wider range of goods and services.
The purchasing power of SNAP benefits is generally lower than $300 in cash.
Additionally, SNAP benefits are subject to certain restrictions, such as the requirement to purchase food items at authorized retailers. These restrictions can limit the options available to SNAP recipients and potentially impact their ability to make the most of their benefits.
SNAP Benefit Restrictions: How Much Is 0 Food Stamps Worth In Cash

The SNAP program has specific rules about what you can purchase with your benefits. These restrictions are designed to ensure that SNAP benefits are used for nutritious food and to prevent abuse of the program.
Allowed Food Items
SNAP benefits can be used to purchase a wide range of food items, including:
- Fruits and vegetables:Fresh, frozen, canned, and dried fruits and vegetables are all eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits. This includes produce like apples, bananas, carrots, spinach, and tomatoes.
- Meat, poultry, and fish:Fresh, frozen, and canned meat, poultry, and fish are all eligible. Examples include beef, chicken, turkey, salmon, and tuna.
- Dairy products:Milk, cheese, yogurt, and other dairy products are eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits.
- Bread and cereals:Bread, pasta, rice, and other grains are eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits.
- Legumes:Beans, lentils, and peas are eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits.
- Eggs:Fresh and frozen eggs are eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits.
- Seeds and plants:Seeds and plants that will produce food are eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits.
Restrictions on Non-Food Items
SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase non-food items, such as:
- Alcohol:SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase alcoholic beverages.
- Tobacco:SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase tobacco products.
- Vitamins and supplements:While some vitamins and supplements are considered food items, most are not eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits.
- Pet food:SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase pet food.
- Cleaning supplies:SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase cleaning supplies.
- Personal care items:SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase personal care items such as soap, shampoo, or toothpaste.
Limitations on Restaurant Meals
SNAP benefits are generally not allowed for purchasing restaurant meals. However, there are some exceptions:
- Home-delivered meals:If a person is unable to cook or shop for themselves due to a disability, they may be eligible to receive home-delivered meals through a SNAP-authorized program. These meals can be purchased with SNAP benefits.
- Meals in a congregate setting:Some SNAP-authorized congregate meal programs, such as those provided by senior centers or community kitchens, allow participants to use SNAP benefits to purchase meals. These programs must be approved by the state SNAP agency.
Note:These restrictions may vary slightly from state to state. It is important to contact your local SNAP office for the most up-to-date information.
SNAP Benefits and Food Security
SNAP benefits play a crucial role in ensuring food security for low-income households across the United States. By providing financial assistance for food purchases, SNAP helps families access nutritious meals and address food insecurity, a critical concern for millions of Americans.
The Impact of SNAP Benefits
SNAP benefits have a significant impact on food security for low-income households. Studies have shown that SNAP participation is associated with improved dietary quality and reduced food insecurity.
SNAP benefits are essential for millions of Americans, particularly in times of economic hardship.
- Reduced Food Insecurity:SNAP benefits significantly reduce the prevalence of food insecurity among low-income households. Research indicates that SNAP participation can reduce food insecurity by up to 50%.
- Improved Dietary Quality:SNAP benefits allow low-income families to purchase a wider variety of foods, leading to improvements in dietary quality. This is particularly important for children, whose growth and development are significantly affected by proper nutrition.
- Increased Food Access:SNAP benefits provide families with the financial resources to access healthy and affordable food options. This is particularly relevant in areas with limited access to grocery stores, known as “food deserts.”
Statistics on SNAP Participation
SNAP is the largest federal nutrition assistance program in the United States, providing food assistance to millions of Americans.
- Number of Participants:In 2022, an average of 41.8 million people participated in SNAP each month, representing about 13% of the U.S. population.
- Families with Children:A significant portion of SNAP participants are families with children. In 2022, nearly 60% of SNAP households included at least one child under the age of 18.
- Economic Impact:SNAP benefits have a substantial economic impact, stimulating local economies by increasing spending in grocery stores and other food-related businesses.
Challenges and Opportunities in Accessing SNAP Benefits
While SNAP benefits offer a lifeline for low-income families, there are challenges and opportunities associated with accessing and utilizing these benefits.
- Eligibility Requirements:Navigating the complex eligibility requirements can be challenging for some individuals and families. This can include meeting income thresholds, asset limitations, and work requirements.
- Stigma and Shame:There is a stigma associated with receiving government assistance, which can discourage some individuals from applying for SNAP benefits, even when they are eligible.
- Limited Access to Technology:Accessing SNAP benefits online or through mobile devices can be difficult for individuals without reliable internet access or digital literacy skills.
- Food Desert Challenges:In food deserts, where access to grocery stores is limited, SNAP benefits may not fully address food security needs. This can lead to reliance on less nutritious food options or increased transportation costs.
- Opportunities for Improvement:There are opportunities to improve access to SNAP benefits, such as streamlining the application process, increasing outreach efforts, and expanding access to technology and digital literacy resources.
Alternative Food Assistance Programs
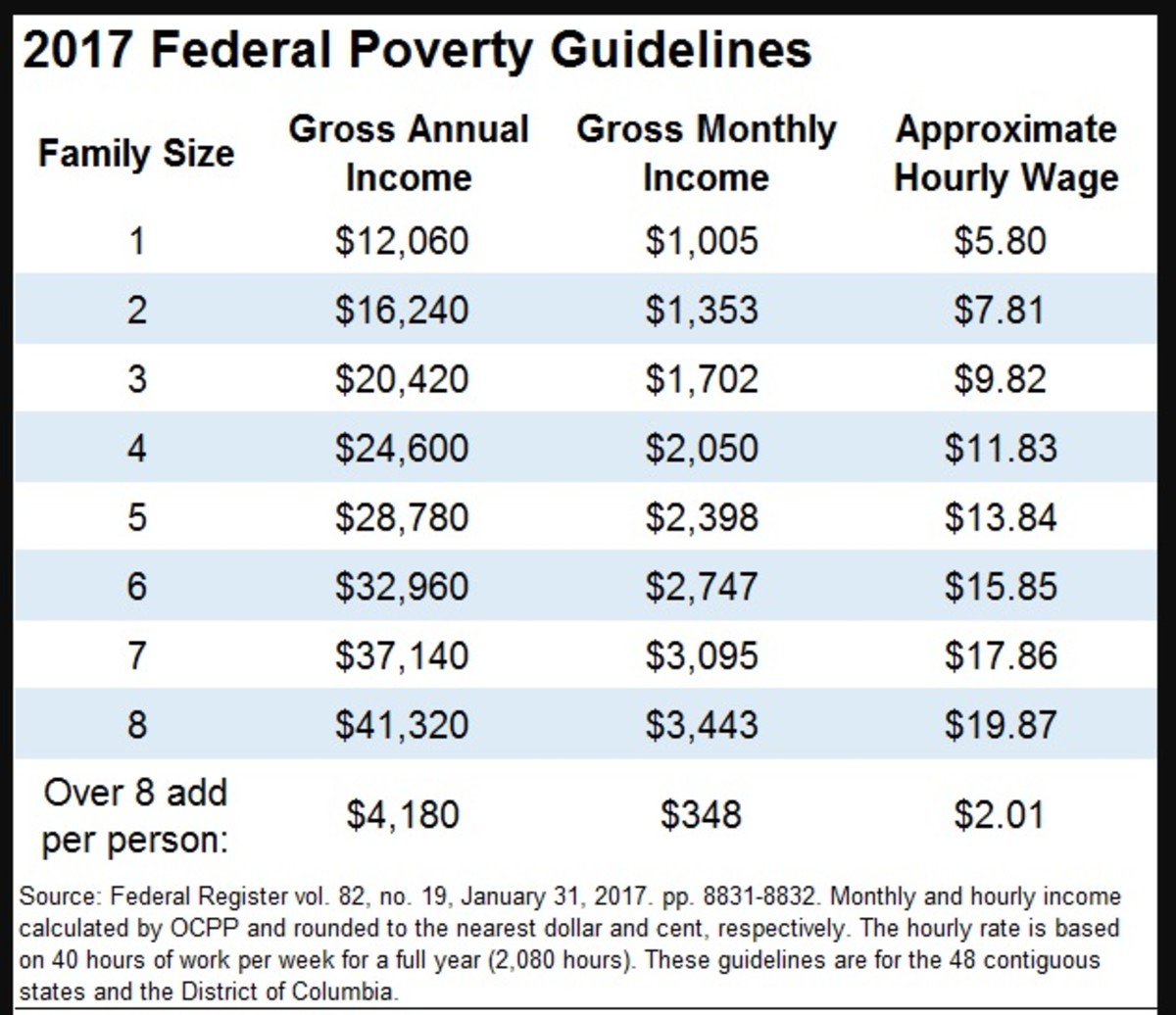
In addition to SNAP, there are other government-funded programs that can provide food assistance to eligible individuals and families. These programs often have different eligibility criteria and offer a range of benefits, catering to specific needs and circumstances.
Comparison of Food Assistance Programs
The following table compares SNAP benefits with other food assistance programs, highlighting key differences in eligibility and benefits:
| Program | Eligibility Criteria | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program) | Low income, meet residency requirements, work or be exempt from work requirements, and other criteria. | Monthly cash benefits for food purchases at authorized retailers. |
| WIC (Women, Infants, and Children) | Low-income pregnant women, postpartum women, breastfeeding women, infants, and children under 5 years old. | Vouchers for specific nutritious foods, such as fruits, vegetables, milk, and cereal. |
| Farmers Market Nutrition Programs | Low-income individuals and families who meet certain income guidelines. | Coupons or vouchers to purchase fresh fruits, vegetables, and other locally grown produce at farmers’ markets. |
Eligibility Criteria for Alternative Programs
Each food assistance program has specific eligibility criteria.
- WIC: To be eligible for WIC, individuals must meet income guidelines and be determined to be at nutritional risk. This includes pregnant women, postpartum women, breastfeeding women, infants, and children under 5 years old.
- Farmers Market Nutrition Programs: These programs typically have income guidelines that are similar to SNAP. Participants must reside in the state or county where the program operates and be eligible for other federal food assistance programs.
Benefits Offered by Alternative Programs
The benefits offered by these programs vary.
- WIC: Participants receive vouchers for specific nutritious foods, such as fruits, vegetables, milk, and cereal. WIC also provides nutrition counseling and breastfeeding support.
- Farmers Market Nutrition Programs: These programs offer coupons or vouchers to purchase fresh fruits, vegetables, and other locally grown produce at farmers’ markets. This helps to promote healthy eating and support local farmers.
Potential Benefits and Limitations of Participating in Multiple Programs
Participating in multiple food assistance programs can provide greater food security and access to a wider range of nutritious foods. However, it’s important to be aware of potential limitations.
- Income Limits: Some programs may have overlapping income requirements, which could limit eligibility for other programs.
- Program Restrictions: Each program has specific restrictions on the types of foods that can be purchased or the locations where they can be used.
- Administrative Burden: Participating in multiple programs can be time-consuming and involve completing multiple applications and documentation.
Final Conclusion
Understanding the value of $300 in SNAP benefits goes beyond simply calculating the cost of groceries. It involves appreciating the impact of these benefits on food security, the challenges faced by low-income households, and the vital role of government assistance in addressing hunger.
While SNAP benefits provide a critical safety net, it’s essential to acknowledge the limitations and potential challenges associated with their utilization. By promoting awareness and advocating for equitable access to food assistance programs, we can work towards a future where food insecurity is a thing of the past.
FAQ Guide
Can I use SNAP benefits to buy prepared meals?
Generally, SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase prepared meals from restaurants or food trucks. However, some states may have pilot programs that allow for limited use of SNAP benefits at certain restaurants.
Are there income limits for receiving SNAP benefits?
Yes, SNAP benefits have income limits based on household size and other factors. You can find the specific income limits for your state on the USDA’s website.
Can I use SNAP benefits to buy alcohol or tobacco?
No, SNAP benefits cannot be used to purchase alcohol, tobacco, or any non-food items.
How often do I receive SNAP benefits?
SNAP benefits are typically issued monthly, but the exact date may vary depending on your state.
Where can I find more information about SNAP benefits?
You can find more information about SNAP benefits on the USDA’s website or by contacting your local SNAP office.






