In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, where threats constantly evolve and adapt, the question of who guards the digital realm takes center stage. Which team focuses on defensive security? This vital force, often unseen but ever-present, stands as the first line of defense against the relentless tide of cyberattacks. Their mission is clear: to protect systems, data, and individuals from the malicious intent that lurks in the shadows of the digital world.
They are the guardians of our digital lives, the silent protectors who ensure our online safety and security.
Defensive security, in its purest form, is the art and science of anticipating, mitigating, and responding to threats that aim to disrupt, compromise, or exploit our digital infrastructure. It involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses everything from implementing robust security measures to fostering a culture of awareness and vigilance among users. These teams are composed of dedicated individuals who possess a deep understanding of cybersecurity principles, threat vectors, and the latest attack techniques.
They are the architects of digital fortresses, constantly evolving their strategies to stay ahead of the ever-changing threat landscape.
Defining Defensive Security

Defensive security is like a fortress, it’s all about protecting what you have. It’s not about attacking or conquering, but about building strong defenses to keep the bad guys out. Think of it like having a really strong password on your phone, or a good lock on your door.
Core Principles of Defensive Security
Defensive security is built on a few key principles. The first is proactive protection, meaning you take steps to prevent attacks before they happen. This could be anything from installing firewalls on your computer to training your employees on cybersecurity best practices. The second principle is layered defense, which means having multiple layers of protection in place. This way, even if one layer is breached, the others will still be there to protect your data.
Finally, risk management is crucial. It’s about identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities and taking steps to mitigate them. This might involve things like conducting regular security audits or implementing incident response plans.
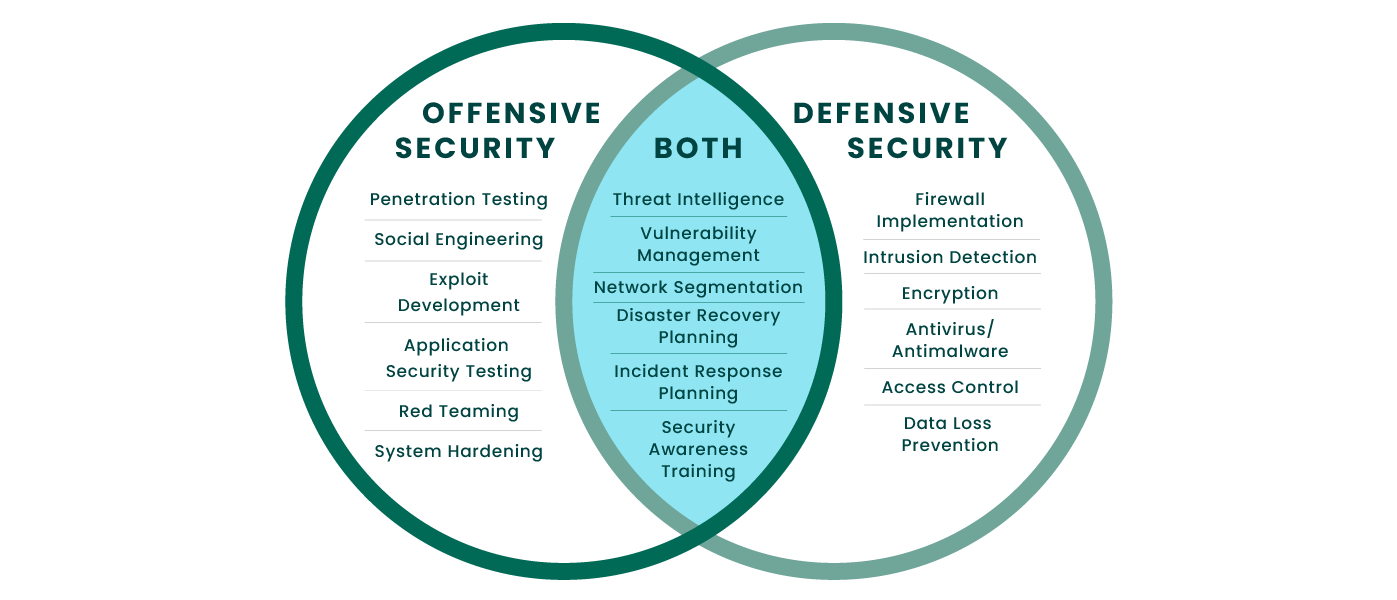
Comparison with Offensive Security
Defensive security and offensive security are two sides of the same coin. Offensive security focuses on finding vulnerabilities and exploiting them, while defensive security aims to prevent those attacks. Here’s a table that highlights the key differences:
| Feature | Defensive Security | Offensive Security |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Protect assets from attacks | Identify and exploit vulnerabilities |
| Methods | Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, security awareness training | Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, social engineering |
| Focus | Prevention and mitigation | Exploitation and analysis |
Real-World Examples of Defensive Security Measures
Here are some real-world examples of defensive security measures in action:
- Firewalls: Firewalls act like a gatekeeper, blocking unauthorized access to your network. They are often used by companies to protect their internal systems from external threats.
- Antivirus software: Antivirus software protects your computer from malware, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans. It scans your system for threats and removes them before they can cause damage.
- Multi-factor authentication: This adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring you to provide more than one form of identification. For example, you might need to enter a password and a code sent to your phone.
- Encryption: Encryption scrambles your data, making it unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have the key to decrypt it. This is a crucial measure for protecting sensitive information, such as financial data or personal health records.
Key Players in Defensive Security
The world of defensive security is a complex ecosystem with many players working together to protect systems and data from cyber threats. These players come from various backgrounds, each contributing their unique expertise and resources.
Types of Organizations Involved in Defensive Security
The organizations involved in defensive security can be broadly categorized into four main types:
- Security Software Vendors: These companies develop and sell security software solutions, including antivirus, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention tools. They play a crucial role in providing the tools and technologies that organizations rely on to protect their systems. Examples include Symantec, McAfee, Trend Micro, and Palo Alto Networks.
- Security Consulting Firms: These firms offer expert advice and services to help organizations improve their security posture. They conduct vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, security audits, and incident response services. They help organizations identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities in their systems and develop strategies to mitigate them. Examples include KPMG, Deloitte, PwC, and Accenture.
- Government Agencies: Government agencies play a significant role in promoting cybersecurity and protecting critical infrastructure. They develop security standards, regulations, and best practices. They also conduct research and development to advance cybersecurity technologies and capabilities. Examples include the National Security Agency (NSA), the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
- Research and Academic Institutions: Universities and research institutions play a vital role in advancing cybersecurity research and education. They conduct research on new threats and vulnerabilities, develop innovative security solutions, and educate the next generation of cybersecurity professionals. Examples include Carnegie Mellon University, MIT, Stanford University, and the University of California, Berkeley.
Roles and Responsibilities of Key Players
Each type of organization has specific roles and responsibilities in protecting systems and data.
| Organization Type | Primary Areas of Focus |
|---|---|
| Security Software Vendors | Developing and selling security software solutions, such as antivirus, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention tools. |
| Security Consulting Firms | Providing expert advice and services to help organizations improve their security posture, including vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, security audits, and incident response services. |
| Government Agencies | Developing security standards, regulations, and best practices; conducting research and development to advance cybersecurity technologies and capabilities; and protecting critical infrastructure. |
| Research and Academic Institutions | Conducting research on new threats and vulnerabilities; developing innovative security solutions; and educating the next generation of cybersecurity professionals. |
Defensive Security Techniques
Defensive security techniques are the methods and strategies used to protect systems and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. These techniques are essential for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information and resources.
Intrusion Prevention Techniques
Intrusion prevention techniques aim to stop attackers from gaining access to systems and networks in the first place. These techniques act as a first line of defense, preventing potential threats from ever reaching their targets.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between a private network and the external world, inspecting incoming and outgoing traffic and blocking any communication that doesn’t meet predefined rules. They are often the first line of defense against external threats.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS constantly monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, alerting administrators to potential attacks. They can be deployed in hardware or software, and are designed to detect known attack patterns and anomalies in network traffic.
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): IPS are a more proactive approach to security, actively blocking malicious traffic before it can reach its target. They use the same principles as IDS but also have the ability to take action to prevent attacks, such as dropping malicious packets or blocking specific IP addresses.
- Network Segmentation: Network segmentation divides a network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting the impact of a breach. This helps to contain the spread of malware and prevent attackers from accessing sensitive data.
Data Protection Techniques
Data protection techniques focus on safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction. These techniques are crucial for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of data, protecting businesses and individuals from financial and reputational damage.
- Data Encryption: Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, making it incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals. This is a fundamental technique for protecting sensitive data, especially when it is transmitted over networks or stored on devices.
- Access Control: Access control mechanisms restrict access to data based on user identity and permissions. This ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information, preventing unauthorized access and misuse.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions monitor data movement and prevent sensitive information from leaving the organization’s control. This helps to protect against data breaches and ensures that confidential data remains within the organization’s boundaries.
- Data Masking: Data masking replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive values, preserving the data structure while protecting the actual information. This is often used for testing and development purposes, where access to real data is not required.
Vulnerability Management Techniques
Vulnerability management techniques aim to identify, assess, and remediate security vulnerabilities in systems and applications. These techniques are essential for proactively addressing weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers, reducing the risk of successful attacks and breaches.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning tools automatically scan systems and applications for known security vulnerabilities. They identify potential weaknesses and provide information on how to remediate them.
- Patch Management: Patch management involves applying security updates and patches to systems and applications to fix vulnerabilities. This is an essential practice for maintaining a secure environment and reducing the risk of attacks.
- Security Auditing: Security audits involve a thorough examination of an organization’s security posture, identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses. They provide a comprehensive assessment of security controls and recommendations for improvement.
- Penetration Testing: Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. This is a proactive approach to security, allowing organizations to discover and address weaknesses before they are exploited.
Implementing a Defensive Security Strategy
Implementing a comprehensive defensive security strategy involves a systematic approach to protecting systems and data. The following flowchart illustrates the typical steps involved:
Step 1: Identify Assets and Risks
Step 2: Develop a Security Policy
Step 3: Implement Security Controls
Step 4: Monitor and Evaluate Security
Step 5: Continuously Improve Security
Challenges in Defensive Security: Which Team Focuses On Defensive Security
Defending against cyberattacks is a constant uphill battle, with the threat landscape evolving rapidly. Defensive security teams face numerous challenges, requiring them to adapt and innovate to stay ahead of the curve.
Impact of Emerging Threats and Technologies
Emerging threats and technologies present significant challenges for defensive security. The rapid adoption of new technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), creates new attack vectors and vulnerabilities. For example, the rise of cloud computing has introduced challenges related to data security and access control, while the proliferation of IoT devices creates a vast network of potential entry points for attackers.
Evolving Landscape of Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and targeted. Attackers are using advanced techniques, such as ransomware, phishing, and social engineering, to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise systems. The use of automated tools and artificial intelligence is further increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of attacks.
Best Practices in Defensive Security

In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, organizations must adopt a proactive approach to defend against emerging threats. Implementing best practices is crucial to bolstering defensive security posture and minimizing vulnerabilities.
Ongoing Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is vital for detecting suspicious activities and potential breaches. By establishing a robust monitoring system, organizations can gain real-time visibility into their network and systems. This allows for early detection of anomalies, enabling prompt response and mitigation of potential threats.
Threat Intelligence, Which team focuses on defensive security
Staying ahead of attackers requires access to up-to-date threat intelligence. By leveraging threat intelligence feeds and resources, organizations can gain insights into emerging threats, attack vectors, and attacker tactics. This knowledge empowers them to proactively implement preventative measures and adjust security controls to mitigate risks.
Incident Response
Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for handling security incidents effectively. A comprehensive plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, including incident detection, containment, investigation, remediation, and recovery. Regular testing and drills ensure the plan is up-to-date and that team members are prepared to respond efficiently.
Layered Security Approach
Implementing a layered security approach provides multiple lines of defense, making it more difficult for attackers to penetrate an organization’s systems. This involves using a combination of security controls at different levels, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, endpoint protection, and user authentication. By creating multiple barriers, organizations can significantly increase the complexity and effort required for attackers to succeed.
The Future of Defensive Security
The landscape of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, and the growing reliance on digital infrastructure. As we navigate this dynamic environment, understanding the key trends shaping the future of defensive security is crucial.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming defensive security by automating threat detection, analysis, and response. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate malicious activity, enabling faster and more accurate threat detection. AI-powered security solutions can also automate tasks such as incident response, vulnerability assessment, and patch management, freeing up security teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
“AI and ML are not just tools for cybersecurity, they are becoming the foundation of it.”
John McAfee, Founder of McAfee
For example, AI-powered intrusion detection systems (IDS) can analyze network traffic in real-time to identify suspicious activity, while ML algorithms can be used to predict potential vulnerabilities and proactively patch them.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Defensive Security
The future of defensive security is shaped by several key trends:
- The Rise of Cloud Security: As organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing, securing cloud environments becomes paramount. This trend necessitates the development of new security solutions and strategies tailored for cloud-based applications and infrastructure.
- The Growing Importance of Zero Trust Security: Zero trust security assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default. This approach requires organizations to implement strong authentication, authorization, and data encryption measures to protect sensitive information.
- The Convergence of IT and Security: The lines between IT and security are blurring as organizations adopt DevSecOps practices, integrating security into the software development lifecycle. This trend requires security professionals to collaborate closely with developers to ensure secure coding practices and early threat detection.
- The Increasing Threat of Insider Threats: As employees increasingly work remotely and have access to sensitive data, the threat of insider threats is growing. Organizations need to implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access to data and mitigate the risks posed by malicious insiders.
- The Rise of Quantum Computing: Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize cybersecurity by enabling the development of new encryption algorithms and breaking existing ones. Organizations need to prepare for the impact of quantum computing on their security posture and invest in quantum-resistant encryption solutions.
Timeline of Defensive Security Technologies and Strategies
The past decade has witnessed significant advancements in defensive security technologies and strategies.
| Year | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| 2013 | The rise of cloud security solutions, such as cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools. |
| 2015 | The adoption of zero trust security principles and the emergence of security information and event management (SIEM) platforms. |
| 2017 | The widespread adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning in cybersecurity, leading to the development of AI-powered threat detection and response solutions. |
| 2019 | The emergence of DevSecOps practices, integrating security into the software development lifecycle. |
| 2021 | The growing importance of insider threat detection and response, and the increasing focus on quantum computing and its implications for cybersecurity. |
In the ongoing battle between defenders and attackers, the importance of a strong defensive security team cannot be overstated. These dedicated individuals are the unsung heroes of the digital age, working tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure our online safety and security. Their vigilance, expertise, and commitment to safeguarding our digital world are crucial in a time when cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and pervasive.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of defensive security teams will only become more critical, ensuring that our data, systems, and lives remain protected in the face of ever-present cyber dangers.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are some common defensive security techniques?
Common defensive security techniques include firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), antivirus software, data encryption, vulnerability scanning, and user awareness training. These techniques work together to create a layered security approach that protects against various threats.
What are some challenges faced by defensive security teams?
Defensive security teams face numerous challenges, including the constant emergence of new threats, the growing complexity of cyberattacks, the shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals, and the need to keep up with rapidly evolving technologies.
What is the role of threat intelligence in defensive security?
Threat intelligence plays a vital role in defensive security by providing insights into emerging threats, attack techniques, and attacker motivations. This information helps security teams to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks.






