Is contract labor cost of goods sold? This question often arises in accounting and financial reporting, particularly for businesses that rely on external labor for production or service delivery. Understanding how contract labor costs are treated within the cost of goods sold (COGS) is crucial for accurate financial reporting and strategic decision-making.
The inclusion of contract labor in COGS is a complex topic influenced by accounting standards, industry practices, and the specific nature of the contracted services. This exploration delves into the intricacies of contract labor costs, examining their impact on COGS, the methods for determining these costs, and the reporting requirements in financial statements. We will also explore the legal and regulatory considerations that businesses must address when utilizing contract labor.
Contract Labor in the Cost of Goods Sold
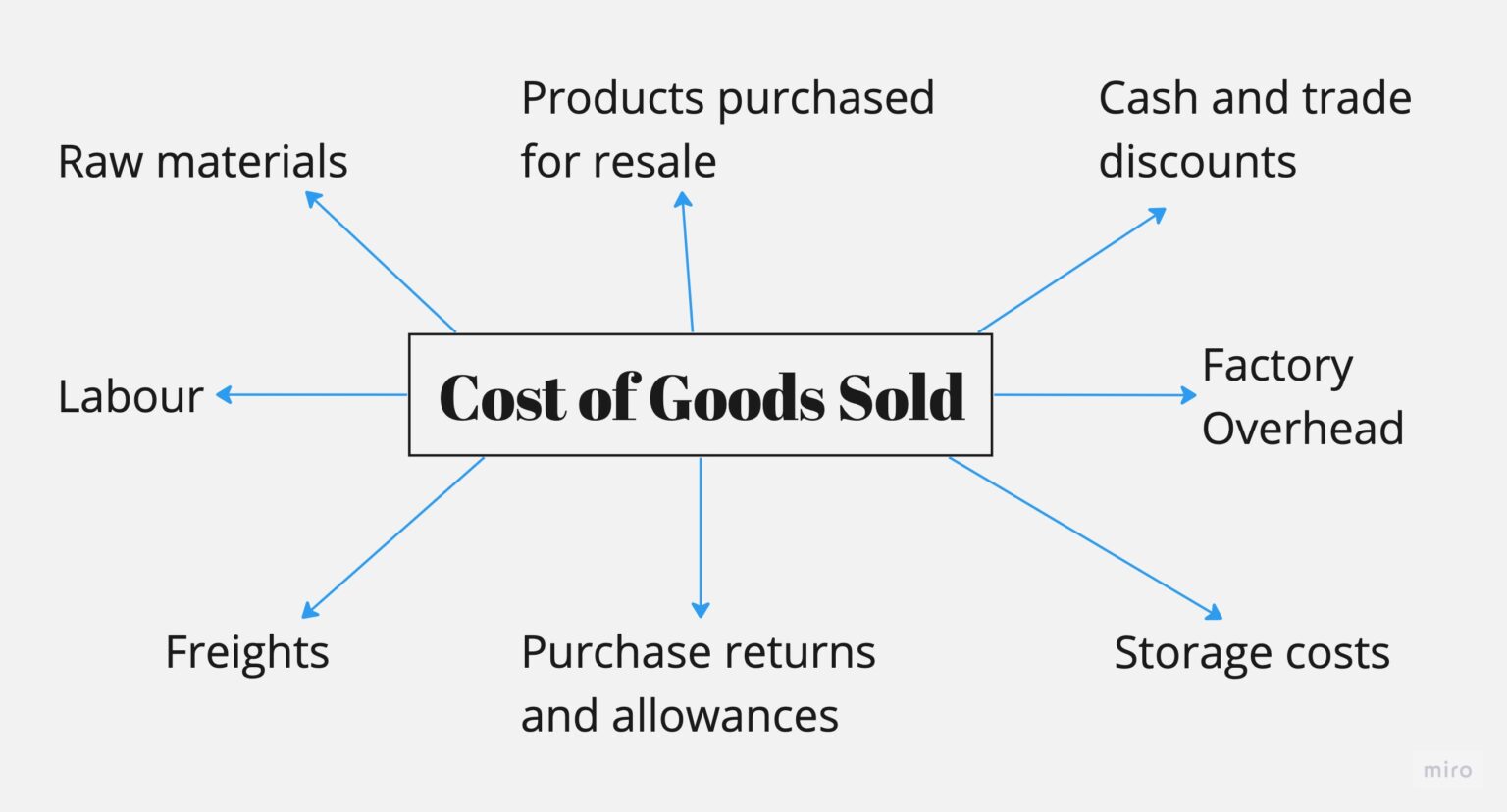
Contract labor is a common practice in many industries, where businesses hire external workers for specific tasks or projects. Understanding how contract labor affects the cost of goods sold (COGS) is crucial for accurate financial reporting and decision-making.
Accounting Treatment of Contract Labor Costs
The accounting treatment of contract labor costs within COGS depends on the nature of the work performed. If the contract labor is directly involved in the production of goods, the costs are typically included in COGS. This means the costs are expensed in the period the goods are sold.
Examples of Industries Where Contract Labor is Significant
Contract labor plays a significant role in various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Companies often use contract labor for specific tasks like assembly, packaging, or quality control.
- Construction: Construction projects heavily rely on contract labor for specialized tasks like plumbing, electrical work, or carpentry.
- Technology: Software development and IT services frequently employ contract labor for project-based work or specialized skills.
- Healthcare: Contract nurses, doctors, and other healthcare professionals are commonly used to meet staffing needs.
Comparison of Accounting Treatment
The following table compares the accounting treatment of contract labor with regular employee wages within COGS:
| Item | Contract Labor | Regular Employee Wages |
|---|---|---|
| Accounting Treatment | Expens | Expens |
| COGS Inclusion | Yes, if directly related to production | Yes, if directly related to production |
| Payroll Taxes | Generally not employer responsibility | Employer responsibility |
| Benefits | Usually not provided by the hiring company | Typically provided by the employer |
Determining Contract Labor Costs for COGS
Accurately determining contract labor costs is crucial for calculating the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and ultimately, your profit margin. Contract labor costs can vary widely depending on the nature of the work, the skill level required, and the duration of the project. This thread explores different methods for determining these costs and factors that influence them.
Methods for Determining Contract Labor Costs
There are several common methods used to determine contract labor costs for COGS, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Time and Materials: This method is based on the actual time spent by the contractor on the project and the materials used. It provides flexibility, especially for projects with uncertain scope or requirements. However, it can lead to cost overruns if the project takes longer than anticipated or if material costs fluctuate.
- Fixed-Price Contracts: In this method, a fixed price is agreed upon upfront, regardless of the actual time and materials used. This provides certainty for both parties, but it can be challenging to estimate the costs accurately, especially for complex projects.
- Percentage-of-Completion: This method involves recognizing revenue and expenses as the project progresses. It is often used for long-term projects and allows for a more accurate reflection of the project’s financial status over time. However, it requires careful tracking of progress and accurate cost estimations.
Factors Influencing Contract Labor Costs
Several factors influence the determination of contract labor costs:
- Scope of Work: The complexity and extent of the work will significantly impact the cost. A large-scale project requiring specialized skills will naturally incur higher costs than a simple task.
- Skill Level Required: The expertise and experience needed for the project directly affect labor costs. Highly skilled professionals with specialized knowledge command higher fees.
- Project Duration: Longer projects generally involve higher costs due to the extended time required for labor and materials. Short-term projects, on the other hand, may have lower overhead costs.
- Location: Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location. Areas with high cost of living or specialized labor markets may have higher contract labor rates.
- Market Conditions: The overall economic climate and demand for labor can also impact contract labor costs. In a competitive market, contractors may offer lower rates to secure projects.
Challenges in Determining Contract Labor Costs
Accurately determining contract labor costs can be challenging due to several factors:
- Unforeseen Circumstances: Projects can encounter unforeseen challenges, such as delays, changes in scope, or material shortages, which can impact labor costs.
- Difficult Cost Estimation: Accurately estimating the time and materials required for complex projects can be difficult, leading to potential cost overruns or underestimations.
- Lack of Transparency: Some contractors may not be transparent about their pricing structure or may include hidden costs, making it difficult to determine the true cost of contract labor.
- Contractual Disputes: Disputes over the scope of work, payment terms, or other contractual issues can arise, leading to additional costs and delays.
Impact of Contract Labor on COGS
Contract labor can significantly impact the cost of goods sold (COGS). It can be a valuable tool for businesses to manage their labor costs, but it also comes with its own set of considerations. Understanding the implications of using contract labor for COGS is crucial for making informed decisions about your workforce.
Financial Implications of Contract Labor vs. Regular Employees
Using contract labor can have distinct financial implications compared to employing regular employees. Contract labor typically involves paying an hourly rate or a fixed fee for the services rendered, which can be advantageous for businesses with fluctuating workloads or short-term projects. In contrast, regular employees receive a salary or hourly wage, along with benefits such as health insurance, paid time off, and retirement contributions.
- Cost of Benefits: Regular employees often come with a higher cost associated with benefits. Contract labor eliminates these expenses, leading to a lower cost per hour worked.
- Flexibility: Contract labor offers greater flexibility, allowing businesses to scale their workforce up or down as needed. This can be beneficial for projects with variable workloads or seasonal demands.
- Tax Advantages: In some cases, businesses may be able to deduct certain expenses related to contract labor, potentially reducing their overall tax burden.
Reporting Contract Labor in Financial Statements: Is Contract Labor Cost Of Goods Sold
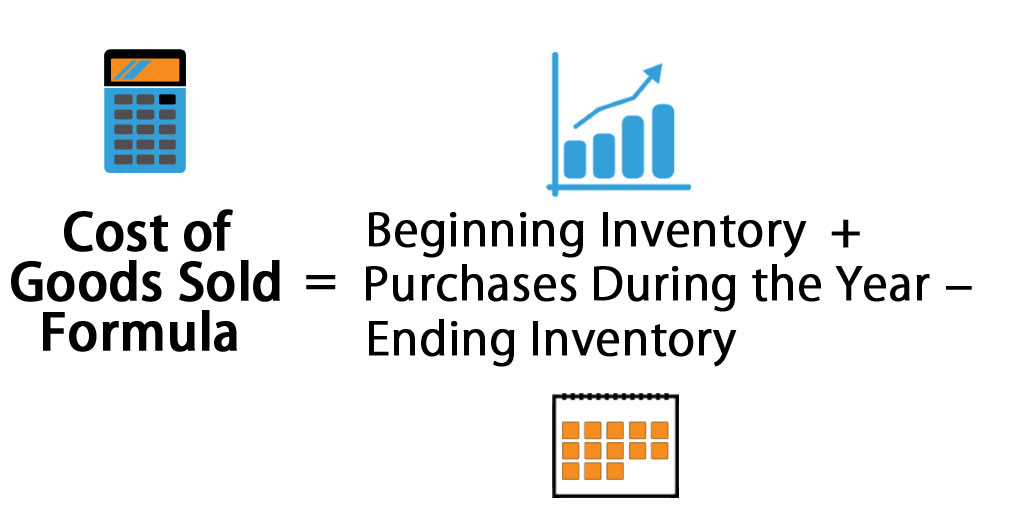
Contract labor costs, as a significant component of the cost of goods sold (COGS), are crucial to understanding a company’s financial performance. Properly reporting contract labor costs in financial statements is essential for transparency and accurate financial reporting.
Reporting Requirements for Contract Labor Costs
Accounting standards require companies to report contract labor costs within the COGS section of the income statement. The specific reporting requirements vary depending on the accounting framework followed by the company (e.g., U.S. GAAP or IFRS). However, the general principle is to ensure that contract labor costs are presented in a manner that is clear, concise, and consistent with the company’s overall accounting policies.
Importance of Disclosure, Is contract labor cost of goods sold
Disclosing the nature and extent of contract labor usage in financial reports is essential for several reasons:
- Transparency: It provides investors, creditors, and other stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of the company’s cost structure and how it utilizes contract labor.
- Comparability: Consistent disclosure allows investors to compare a company’s performance with its peers and identify any significant differences in their reliance on contract labor.
- Financial Analysis: Analysts can use the information on contract labor to assess the company’s operational efficiency, cost management strategies, and potential risks associated with its reliance on external labor.
Examples of Contract Labor Cost Presentation
Contract labor costs are typically presented in the COGS section of the income statement, either as a separate line item or grouped with other direct labor costs.
- Separate Line Item: Companies may choose to present contract labor costs as a separate line item, particularly if it represents a significant portion of their COGS. This provides a clear view of the company’s reliance on contract labor.
- Grouped with Direct Labor: Alternatively, companies may group contract labor costs with other direct labor costs, such as wages and salaries of permanent employees. This approach is common if contract labor represents a smaller proportion of the total direct labor costs.
Companies should also disclose the nature of the contract labor services used, such as manufacturing, engineering, or IT services. They should also disclose the percentage of COGS attributable to contract labor, providing a measure of its relative importance.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations

The use of contract labor in the calculation of cost of goods sold (COGS) presents unique legal and regulatory considerations. Understanding these complexities is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal risks.
Compliance with Labor Laws and Regulations
It is essential for businesses to adhere to labor laws and regulations when utilizing contract labor. These laws vary significantly by jurisdiction and can impact the classification of workers, wage and hour requirements, and benefits provisions.
- Independent Contractor vs. Employee Classification: The distinction between independent contractors and employees is critical. Misclassification can lead to significant penalties. The IRS, for instance, has established specific guidelines to determine worker classification, focusing on factors such as control, opportunity for profit, and investment.
- Wage and Hour Laws: Businesses must ensure they comply with federal and state wage and hour laws, including minimum wage, overtime pay, and recordkeeping requirements. This applies to both employees and contract workers, as misclassification can result in back pay obligations and penalties.
- Benefits Provisions: Contract workers may not be entitled to the same benefits as employees, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and unemployment insurance. However, businesses should be aware of any state or local regulations that may mandate certain benefits for contract workers.
Best Practices for Managing Contract Labor Costs
Effectively managing contract labor costs within the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is crucial for maintaining profitability and achieving financial stability. Implementing best practices ensures that businesses optimize their contract labor expenditures, maximizing value and minimizing risks.
Best Practices for Managing Contract Labor Costs
A comprehensive checklist of best practices for managing contract labor costs within COGS provides a framework for streamlining processes and achieving cost-effectiveness.
- Establish a Clear Contract Labor Policy: Defining a comprehensive contract labor policy Artikels the company’s approach to utilizing contract labor, encompassing approval processes, cost control measures, and compliance requirements. This policy serves as a guide for all stakeholders involved in managing contract labor, ensuring consistency and adherence to best practices.
- Implement a Robust Contract Management System: Utilizing a robust contract management system enables efficient tracking, monitoring, and administration of contract labor agreements. This system helps to ensure that contracts are properly negotiated, reviewed, and updated, minimizing potential risks and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Conduct Thorough Vendor Due Diligence: Before engaging a contract labor provider, conducting thorough due diligence is essential to assess their capabilities, reliability, and financial stability. This involves reviewing their track record, references, and financial statements to ensure they meet the company’s quality and performance standards.
- Negotiate Favorable Contract Terms: Negotiating favorable contract terms is crucial for minimizing contract labor costs. This involves clearly defining the scope of work, payment terms, performance metrics, and termination clauses to ensure a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Monitor Contract Labor Performance: Regularly monitoring contract labor performance is essential to ensure that they meet the company’s expectations. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), conducting performance reviews, and addressing any issues promptly to maintain high levels of quality and productivity.
- Optimize Contract Labor Utilization: Optimizing contract labor utilization involves carefully planning and scheduling contract labor assignments to maximize their effectiveness. This may involve using time and attendance tracking systems, scheduling work based on peak demand periods, and utilizing flexible staffing arrangements to meet fluctuating business needs.
- Implement Cost Control Measures: Implementing cost control measures is essential for managing contract labor costs effectively. This may involve negotiating competitive rates, reviewing invoices for accuracy, and implementing cost-saving strategies such as bulk purchasing or sharing resources with other companies.
Evaluating and Selecting Contract Labor Providers
Evaluating and selecting the right contract labor providers is crucial for ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Assess Provider Capabilities: Evaluate the provider’s experience, expertise, and resources to determine their ability to meet the company’s specific needs. Consider their industry knowledge, technical skills, and track record of successful projects.
- Review Provider References: Contact previous clients to gain insights into the provider’s performance, reliability, and customer satisfaction. This provides valuable feedback on their work quality, communication, and ability to meet deadlines.
- Evaluate Provider Financial Stability: Assess the provider’s financial health to ensure their ability to fulfill contractual obligations. Review their financial statements, credit rating, and history of payment performance to mitigate risks.
- Compare Provider Rates: Obtain quotes from multiple providers to compare rates and negotiate favorable terms. Consider the overall value proposition, including quality, service, and experience, rather than focusing solely on the lowest price.
- Assess Provider Compliance: Verify that the provider meets all relevant legal and regulatory requirements, including labor laws, safety regulations, and environmental standards. This ensures compliance and minimizes potential legal risks.
Negotiating Favorable Contract Terms
Negotiating favorable contract terms is crucial for minimizing contract labor costs and ensuring a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Define Scope of Work: Clearly define the scope of work to avoid ambiguity and ensure that the provider understands the specific tasks and deliverables required. This minimizes the risk of disputes or additional costs arising from unclear expectations.
- Establish Payment Terms: Negotiate payment terms that are fair and reasonable, considering factors such as payment frequency, milestones, and payment methods. This ensures timely payment and avoids potential cash flow issues.
- Set Performance Metrics: Establish clear performance metrics to measure the provider’s effectiveness and ensure they meet the company’s quality standards. This may include metrics such as on-time delivery, accuracy, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
- Include Termination Clauses: Include termination clauses in the contract to provide a clear process for ending the agreement under specific circumstances. This protects both parties and ensures a smooth transition if the relationship needs to be terminated.
- Consider Incentives and Penalties: Incorporate incentives for exceeding performance targets and penalties for failing to meet agreed-upon standards. This motivates the provider to deliver high-quality work and minimizes the risk of subpar performance.
In conclusion, understanding the accounting treatment of contract labor within COGS is essential for businesses that rely on external labor. By accurately determining contract labor costs, businesses can ensure their financial statements reflect the true cost of goods sold. This knowledge empowers informed decision-making regarding the use of contract labor and its impact on profitability. It is also crucial to remain vigilant regarding legal and regulatory compliance when utilizing contract labor to avoid potential legal risks.
Essential Questionnaire
How do I determine the cost of contract labor for COGS?
The cost of contract labor for COGS is typically determined based on the terms of the contract, which may include time and materials, fixed-price contracts, or percentage-of-completion methods. Factors like the scope of work, skill level required, and project duration also influence the cost.
What are the legal and regulatory considerations for contract labor?
Businesses must comply with labor laws and regulations regarding contract labor, including ensuring proper classification of workers and adherence to minimum wage and overtime laws. Misclassifying contract labor can lead to legal penalties.
What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of using contract labor for COGS?
Benefits include cost savings, flexibility, and access to specialized skills. Drawbacks include potential quality control issues, lack of long-term commitment, and potential legal risks.






