What is options per contract fee? It’s a crucial aspect of options trading that directly affects your profitability. Every time you buy or sell an options contract, you’ll encounter a fee, often referred to as a “per-contract fee.” This fee, along with other costs like commissions and exchange fees, adds up and can significantly impact your trading outcomes.
Understanding options per contract fees is essential for any options trader, as it directly influences your potential profits and losses. This fee is calculated based on various factors, including the underlying asset, contract type, and brokerage platform you choose. By understanding these factors and how they affect your trading costs, you can make more informed decisions and optimize your trading strategies.
Understanding Options Contracts: What Is Options Per Contract Fee

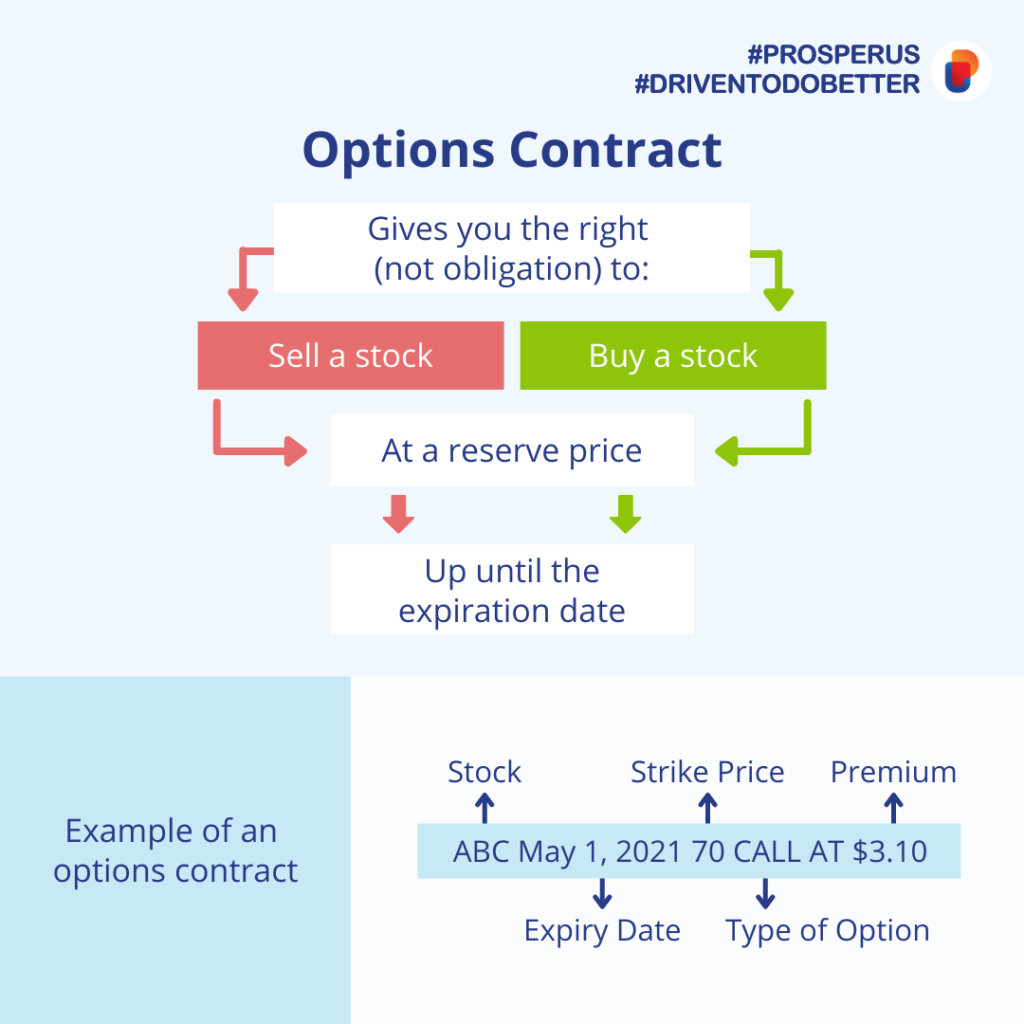
Options contracts are powerful financial instruments that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. They are popular among investors seeking to leverage their capital and manage risk, offering a unique way to profit from market fluctuations.
Call and Put Options
Call and put options are the two main types of options contracts. They offer different strategies for investors based on their market outlook.
- Call options give the holder the right to buy an underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) before the expiration date. Investors buy call options when they anticipate the price of the underlying asset to rise, aiming to profit from the difference between the strike price and the market price at the time of exercise.
- Put options give the holder the right to sell an underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) before the expiration date. Investors buy put options when they anticipate the price of the underlying asset to fall, aiming to profit from the difference between the strike price and the market price at the time of exercise.
Key Elements of an Options Contract
Understanding the key elements of an options contract is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
- Strike Price: This is the predetermined price at which the holder can buy or sell the underlying asset. It is set at the time the option is purchased.
- Expiration Date: This is the final date on which the option can be exercised. After this date, the option expires and becomes worthless.
- Underlying Asset: This is the asset that the option contract is based on. It can be a stock, index, commodity, or currency.
- Premium: This is the price paid by the buyer of the option to acquire the right to buy or sell the underlying asset. It is a non-refundable payment that represents the value of the option.
Buying and Selling Options Contracts
The way an investor interacts with an options contract depends on whether they are buying or selling the option.
- Buying an option gives the investor the right to exercise the contract, but they are not obligated to do so. They pay a premium for this right. Buying options is a bullish strategy for call options and a bearish strategy for put options.
- Selling an option obligates the investor to fulfill the contract if the buyer exercises it. They receive a premium for this obligation. Selling options is a bearish strategy for call options and a bullish strategy for put options.
Options Per Contract Fee
Every time you buy or sell an options contract, your brokerage will charge you a fee. This fee is known as the “options per contract fee,” and it’s an important factor to consider when evaluating the profitability of your trades.The options per contract fee is a fixed cost that you pay for the privilege of trading options. It’s typically charged per contract, regardless of the price of the underlying asset or the type of option you’re trading.
Factors Influencing Options Per Contract Fee, What is options per contract fee
The options per contract fee can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Underlying Asset: The type of underlying asset can affect the fee. For example, options on stocks may have different fees than options on ETFs or indices.
- Contract Type: The type of option contract (e.g., call or put) can also influence the fee. Some brokerages may charge different fees for different contract types.
- Brokerage: Different brokerages have different fee structures. Some brokerages offer lower fees than others, so it’s essential to compare fees before choosing a brokerage.
Calculating Options Per Contract Fee
The options per contract fee is typically calculated based on the following formula:
Options per contract fee = (Fee per contract) x (Number of contracts)
For example, if your brokerage charges $1 per contract and you buy 10 contracts, your options per contract fee would be $10.
Impact of Options Per Contract Fee on Profitability
The options per contract fee can have a significant impact on the profitability of your trades. It’s essential to factor in the fee when calculating your potential profits and losses.For example, let’s say you buy a call option for $100 and the underlying asset price rises to $120. You would make a profit of $20, but after deducting the options per contract fee, your actual profit would be lower.It’s also important to note that the options per contract fee can eat into your profits, especially if you’re trading a large number of contracts or options with a low premium.
Types of Options Fees
When you trade options, you’ll encounter various fees that contribute to the overall cost of your transactions. These fees vary depending on the brokerage platform you use and the specific options contract you’re trading. Understanding these fees is crucial for making informed trading decisions and maximizing your profits.
Commission Fees
Commission fees are charged by your brokerage platform for executing your options trades. These fees can be a flat rate per contract, a percentage of the transaction value, or a combination of both. Some brokers offer commission-free options trading, while others charge tiered pricing based on the volume of your trades.
Exchange Fees
Exchange fees are levied by the options exchanges where your contracts are traded. These fees are typically charged per contract and vary depending on the underlying asset and the type of options contract. The fees cover the exchange’s operational costs and contribute to the overall liquidity of the market.
Regulatory Fees
Regulatory fees are charged by government agencies to oversee and regulate the options market. These fees are typically a small percentage of the transaction value and are designed to ensure fair and transparent trading practices.
Comparing Fee Structures
Brokerage platforms often offer different fee structures for options trading. Some brokers may charge lower commission fees but higher exchange fees, while others may offer a more balanced approach. It’s essential to compare the fee structures of various brokers before choosing one that best suits your trading style and needs.
Typical Options Contract Fees
The following table Artikels the typical fees associated with options contracts, including examples of fees for different brokers:| Broker | Commission Fee | Exchange Fee | Regulatory Fee | Total Fee ||—|—|—|—|—|| Broker A | $0.50 per contract | $0.75 per contract | $0.10 per contract | $1.35 per contract || Broker B | $0.25 per contract | $1.00 per contract | $0.15 per contract | $1.40 per contract || Broker C | Free | $0.85 per contract | $0.10 per contract | $0.95 per contract |
Note: These fees are for illustrative purposes only and may vary depending on the specific options contract, the underlying asset, and the brokerage platform. It’s always advisable to check the fee schedule of your chosen broker before placing any trades.
Calculating Total Costs

Understanding the total cost of an options contract is crucial for informed decision-making. The total cost includes the premium, fees, and any other applicable charges. This section will guide you through calculating the total cost of an options trade, including the per-contract fee.
Calculating Total Cost
The total cost of an options trade can be calculated by adding the premium, fees, and any other applicable charges. Here is a step-by-step guide to determine the total cost of an options trade:
1. Premium
This is the price you pay to buy an option contract. The premium is determined by market forces and reflects the perceived value of the underlying asset and the time remaining until expiration.
2. Fees
Brokerage fees, exchange fees, and regulatory fees are typically charged for each options contract traded.
3. Options Per Contract Fee
This is a fee charged by some brokers for each options contract traded. It is typically a fixed amount per contract.
4. Other Charges
Some brokers may charge additional fees, such as margin interest, for holding options contracts. Example:Let’s assume you want to buy one call option contract on a stock with a premium of $5.00 per share, and the strike price is $100.Your broker charges a $10.00 commission per contract, and there is a $1.00 options per contract fee. The total cost of this trade would be:* Premium: $5.00 per share100 shares per contract = $500.00
Fees
$10.00 (commission) + $1.00 (options per contract fee) = $11.00
Total Cost
$500.00 (premium) + $11.00 (fees) = $511.00
Therefore, the total cost of this options trade would be $511.00.
Total Cost = Premium + Fees + Options Per Contract Fee + Other Charges
Impact on Profitability
Options per contract fees, though seemingly small, can significantly impact the profitability of your options trades. These fees, often charged by brokerage firms, directly reduce your potential profits and amplify your potential losses. Understanding how these fees work and implementing strategies to minimize their impact is crucial for maximizing your trading success.
Impact of Fees on Profitability
Options per contract fees directly impact the profitability of options trades by reducing the potential profits and increasing the potential losses. For instance, consider a scenario where you buy a call option for $1.00 per share with a strike price of $100.00 and a premium of $5.00. You expect the stock to rise to $110.00.
The maximum profit you can make on this trade is $5.00 per share, or $500.00 for a contract of 100 shares.
However, if your brokerage charges a $1.00 per contract fee, your net profit is reduced to $4.00 per share, or $400.00 for a contract of 100 shares.
The same fee can also amplify your losses if the stock price falls below your strike price.
For example, if the stock price falls to $95.00, your loss would be $5.00 per share, or $500.00 for a contract of 100 shares. With a $1.00 per contract fee, your net loss would be $6.00 per share, or $600.00 for a contract of 100 shares.
Strategies for Minimizing Fees
- Choose a Broker with Lower Fees: Compare fees across different brokerage platforms and select one that offers lower per-contract fees. Some brokers offer tiered fee structures, where the fees decrease with increased trading volume.
- Trade Options with Higher Premiums: Higher premium options generally offer greater potential profits, which can offset the impact of per-contract fees. However, it’s essential to remember that higher premiums also mean higher potential losses.
- Trade Options with Longer Expirations: Options with longer expirations typically have higher premiums, which can help offset per-contract fees. However, it’s crucial to consider the increased risk associated with longer expirations.
- Trade Options with Higher Strike Prices: Options with higher strike prices generally have lower premiums, which can help minimize the impact of per-contract fees. However, it’s essential to consider the reduced potential profits.
Comparing Options Trading Fees
Choosing the right brokerage platform for options trading is crucial, as fees can significantly impact your profitability. Understanding the different fee structures and comparing them across various platforms is essential to make an informed decision.
Comparison of Options Trading Fees
Options trading fees can vary widely depending on the brokerage platform. Here’s a table comparing the fees charged by some popular platforms:
| Brokerage Platform | Per-Contract Fee | Minimum Fee | Other Fees | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD Ameritrade | $0.65 | $0.65 | $0 per trade, inactivity fees may apply | Offers a wide range of educational resources and tools for options traders. |
| Fidelity | $0.65 | $0.65 | $0 per trade, inactivity fees may apply | Known for its low-cost trading and comprehensive research capabilities. |
| Interactive Brokers | $0.05 | $1 | Variable commissions, tiered fee structure based on trading volume | Offers a highly customizable trading platform and advanced tools for experienced traders. |
| E*TRADE | $0.65 | $0.65 | $0 per trade, inactivity fees may apply | Provides a user-friendly platform and a wide selection of educational resources. |
Pros and Cons of Different Brokerage Options
The best brokerage platform for you will depend on your individual trading style, frequency, and volume.
- Low-Cost Brokers: Platforms like Fidelity and TD Ameritrade offer low per-contract fees, making them attractive for frequent traders. However, they may have limited advanced features or research tools.
- Discount Brokers: E*TRADE and other discount brokers offer a balance between low fees and decent features. They can be a good option for traders who value simplicity and affordability.
- Professional Platforms: Interactive Brokers, with its tiered fee structure, caters to high-volume traders and professional investors. Its advanced features and tools come at a higher cost.
Important Note: This table is for illustrative purposes only and may not reflect the most up-to-date information. It’s essential to check the current fee structure of each brokerage platform before making a decision.
Considerations for Options Traders
Understanding options per contract fees is crucial for options traders, as it directly impacts the profitability of their strategies. These fees, often charged by brokerage platforms, can eat into potential gains or even turn a profitable trade into a losing one. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the impact of fees when analyzing potential trades and evaluating the overall cost of trading options.
The Impact of Options Fees on Trading Strategies
Different options trading strategies carry varying levels of risk and potential reward. The impact of options per contract fees can significantly influence the outcome of these strategies. For example, high-frequency trading strategies that involve numerous trades may be particularly sensitive to fees, as the cumulative effect of these charges can erode profits. On the other hand, long-term options strategies with lower trading frequency may be less affected by fees.
Choosing the Right Brokerage Platform
The options trading platform you choose can have a significant impact on your overall trading costs. Some platforms offer lower per-contract fees, while others provide other benefits, such as advanced trading tools or research capabilities. When selecting a brokerage platform, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Per-contract fees: Compare the fees charged by different platforms for options contracts. Some platforms may offer tiered pricing based on trading volume or account balance.
- Other fees: In addition to per-contract fees, platforms may charge other fees, such as inactivity fees, account maintenance fees, or withdrawal fees. It’s important to understand all fees associated with a platform before opening an account.
- Trading platform features: Consider the features and tools offered by different platforms, such as charting capabilities, order types, and research resources. These features can impact your trading efficiency and decision-making process.
- Customer support: It’s essential to choose a platform with reliable customer support in case you encounter any issues. Look for platforms with 24/7 support options and a strong reputation for customer service.
It’s important to remember that the lowest fee isn’t always the best option. Consider the overall value proposition of a platform, including its fees, features, and customer support, when making your decision.
Options per contract fees are a vital part of the options trading landscape, influencing your profitability and overall trading experience. By carefully considering the fee structures of different brokerages and understanding the factors that influence these fees, you can make more informed decisions and maximize your trading potential. Remember, a thorough understanding of options per contract fees is crucial for navigating the complexities of options trading and achieving your financial goals.
FAQ Section
What are some examples of options per contract fees?
Options per contract fees can vary depending on the brokerage platform. Some common examples include fees ranging from $0.50 to $2.00 per contract, but these can fluctuate based on the specific contract and broker.
How do options per contract fees affect my profits?
High options per contract fees can eat into your potential profits. For example, if you make a $100 profit on a trade but pay $2.00 per contract in fees, your net profit will be reduced to $98.00. Conversely, if you incur a loss, these fees will amplify the impact on your trading account.
Are there ways to minimize options per contract fees?
Yes, there are several ways to minimize options per contract fees. You can choose a brokerage platform with lower fees, trade in higher volume to potentially qualify for discounted rates, or consider alternative options trading strategies that minimize the number of contracts traded.
Can I negotiate options per contract fees with my broker?
While you might not be able to negotiate the fees directly, you can explore different brokerage platforms to find those with competitive fee structures. Some brokers offer tiered pricing based on your trading volume, which can lead to lower fees as you trade more frequently.






