What is the highest income for food stamps 2024 – What is the highest income for food stamps in 2024? This question is on the minds of many individuals and families seeking assistance with food costs. The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, offers financial aid to eligible households to purchase groceries.
However, the eligibility criteria for SNAP, including income limits, are not static and can vary depending on several factors.
To understand the highest income for SNAP eligibility in 2024, we must first grasp the general eligibility requirements. These include factors like household size, income levels, and resources. Income limits are determined based on household size, with specific thresholds established for each size category.
For example, a one-person household may have a different income limit compared to a two-person or three-person household. It’s important to note that income is calculated considering earned income, unearned income, and certain deductions.
Eligibility for SNAP Benefits in 2024: What Is The Highest Income For Food Stamps 2024
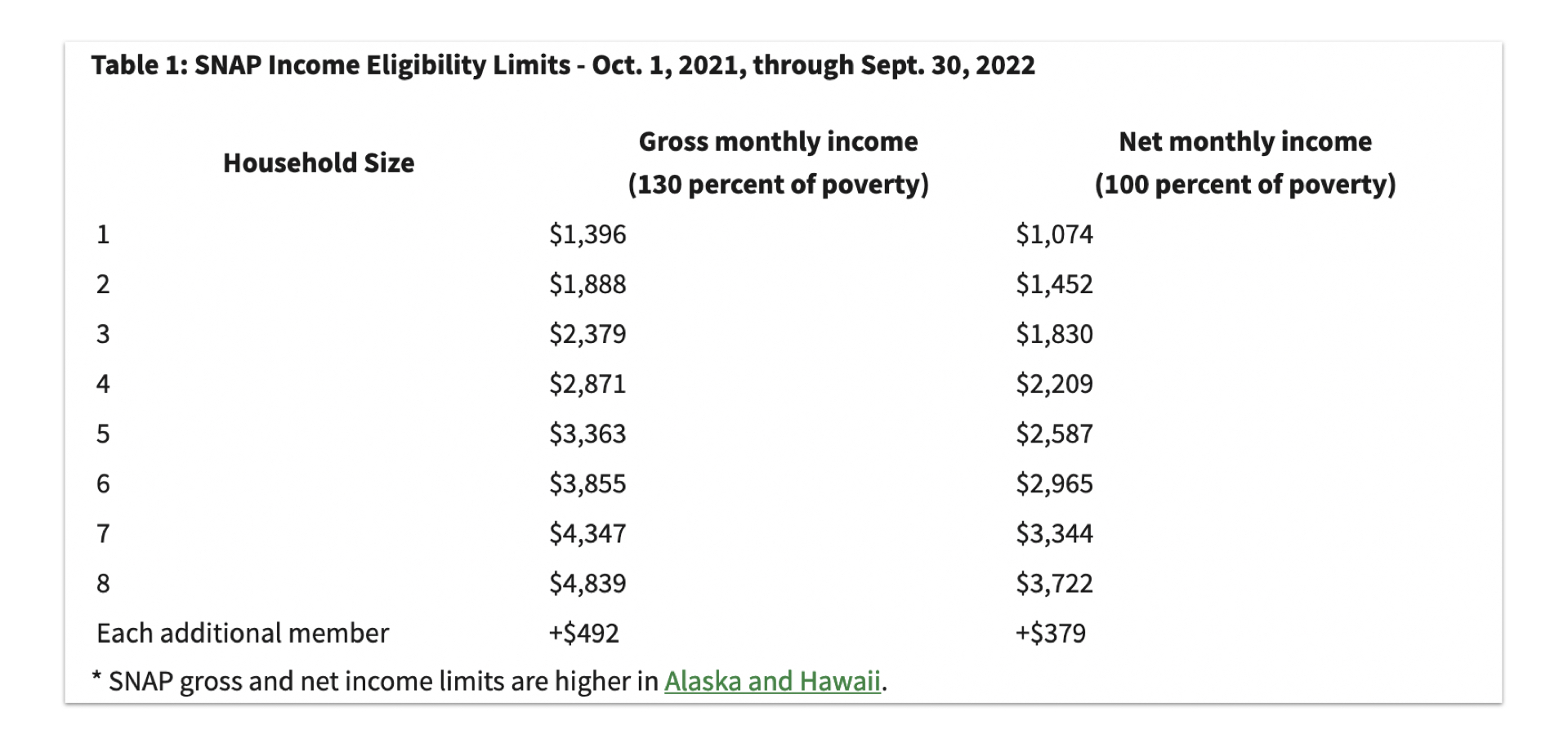
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as food stamps, is a federal program that provides financial assistance to low-income households for food purchases. Eligibility for SNAP benefits is determined by factors such as income, household size, and resources.
General Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for SNAP benefits in 2024, individuals and households must meet specific criteria related to income, resources, and other factors. These criteria are designed to ensure that SNAP benefits are targeted towards those who are most in need of assistance.
Income Limits for SNAP Benefits
SNAP income limits vary based on household size. The following table provides an overview of the maximum gross monthly income limits for different household sizes in 2024:
| Household Size | Gross Monthly Income Limit |
|---|---|
| 1 Person | $2,044 |
| 2 People | $2,759 |
| 3 People | $3,473 |
Income Calculation for SNAP Eligibility
To determine SNAP eligibility, income is calculated by considering both earned and unearned income.
Earned Income
Earned income includes wages, salaries, tips, and other income received from employment.
Unearned Income
Unearned income encompasses income received from sources other than employment, such as:
- Social Security benefits
- Unemployment benefits
- Child support
- Alimony
- Pensions
- Interest and dividends
Deductions
Several deductions can be applied to income when calculating SNAP eligibility. These deductions help to ensure that the program is accessible to individuals and households with certain expenses. Some common deductions include:
- A standard deduction for each household
- Deductions for work-related expenses
- Deductions for child care expenses
- Deductions for medical expenses
- Deductions for housing expenses
The SNAP income calculation formula is:Gross Monthly Income
Deductions = Net Monthly Income
Income Limits and the “Highest Income” for SNAP

It is important to understand that the “highest income” for SNAP eligibility is not a fixed number. Instead, it varies based on household size and other factors, such as state of residence. The SNAP program has specific income guidelines that determine who is eligible for benefits.
State and Federal Guidelines
The income limit for SNAP is determined by a combination of state and federal guidelines. The federal government sets a national poverty level, which is used to calculate the income eligibility threshold for SNAP. However, states have the option to set their own income limits, which can be higher or lower than the federal guideline.
These guidelines are subject to change from year to year, based on factors like inflation and economic conditions.
Income Limits Vary Across States
For instance, in 2024, the maximum gross monthly income for a household of four in California is $3,540, while in Alabama, it is $2,964. These differences in income limits reflect the varying cost of living and economic conditions across different states.
It is crucial to remember that the income limit for SNAP is not the only factor determining eligibility. Other factors, such as assets and expenses, are also considered.
Factors Influencing SNAP Income Limits

The maximum income for SNAP benefits is not a fixed number and can vary depending on several factors. These factors play a crucial role in determining the eligibility criteria for SNAP benefits and the “highest income” that qualifies for assistance.
State-Specific Adjustments
States have the authority to adjust the federal SNAP income limits to reflect their unique circumstances. These adjustments aim to address regional differences in the cost of living and other factors that might impact a household’s ability to afford food.
- For instance, states with higher housing costs may adjust the income limits upward to ensure that households in those areas can meet their basic needs.
- Conversely, states with lower cost of living might adjust the income limits downward, reflecting the lower expenses in those regions.
Cost-of-Living Differences, What is the highest income for food stamps 2024
The cost of living can vary significantly across different geographic regions. This variation can impact the income limits for SNAP benefits, as it influences the amount of money a household needs to meet its basic food needs.
- Areas with higher costs of living, such as major metropolitan cities, may have higher income limits to account for the increased expenses associated with food, housing, and other necessities.
- Rural areas, on the other hand, may have lower income limits due to lower costs of living.
Changes in Federal Guidelines
The federal government periodically updates the SNAP income guidelines to reflect changes in the economy and other relevant factors. These updates can impact the income limits for SNAP benefits, potentially increasing or decreasing the amount of income a household can earn while still qualifying for assistance.
- For example, changes in the federal poverty level can lead to adjustments in the SNAP income limits.
- Inflation can also influence the SNAP income limits, as the cost of food and other necessities rises.
Temporary Programs or Policies
The federal government may implement temporary programs or policies that affect SNAP income limits. These programs often aim to address specific economic challenges or emergencies.
- During a pandemic or natural disaster, the government may temporarily increase SNAP benefits or adjust income limits to provide additional support to households facing hardship.
- Temporary policies might also be implemented to address specific needs, such as increasing SNAP benefits for families with young children.
Last Recap

Navigating the complexities of SNAP eligibility can be challenging, but it’s crucial to remember that resources are available to help. Individuals can consult state SNAP websites, the federal SNAP website, or local food banks and community organizations for detailed information and personalized guidance.
By understanding the eligibility criteria, income limits, and available resources, individuals can make informed decisions about accessing SNAP benefits and ensuring access to nutritious food.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between earned and unearned income?
Earned income refers to income from employment, such as wages or salaries. Unearned income encompasses income sources other than employment, such as interest from savings accounts, dividends, or government benefits like Social Security.
Can I still be eligible for SNAP if I have a car?
SNAP eligibility is not determined by car ownership. The program focuses on income and asset limits. However, certain asset limits may apply, and individuals should consult official SNAP resources for specific details.
Are there any time limits for receiving SNAP benefits?
While there are no specific time limits for receiving SNAP benefits, eligibility is reassessed periodically. Individuals must report any changes in their income, household size, or other circumstances that may affect their eligibility.






